
Hajime Ishihara: Constructive reverse mathematics an introduction and recent results
The lecture was held within the framework of the Hausdorff Trimester Program: Types, Sets and Constructions. Abstract: This talk presents an introduction to constructive reverse mathematics (CRM) with some recent results. The aim of CRM is to classify various theorems in intuitionistic, c
From playlist Workshop: "Proof, Computation, Complexity"
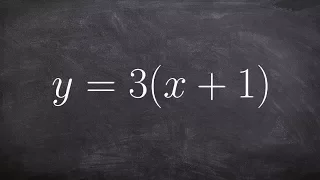
Learn step by step how to find the inverse of an equation, then determine if a function or not
👉 Learn how to find the inverse of a linear function. A linear function is a function whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 1. The inverse of a function is a function that reverses the "effect" of the original function. One important property of the inverse of a function is that whe
From playlist Find the Inverse of a Function
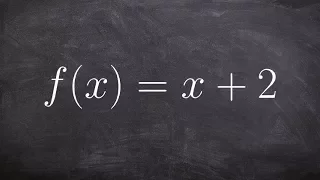
How does the graph of a function compare to it's inverse
👉 Learn how to find the inverse of a linear function. A linear function is a function whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 1. The inverse of a function is a function that reverses the "effect" of the original function. One important property of the inverse of a function is that whe
From playlist Find the Inverse of a Function
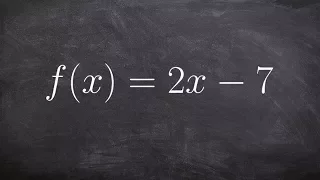
Learn how to find the inverse of a linear equation step by step
👉 Learn how to find the inverse of a linear function. A linear function is a function whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 1. The inverse of a function is a function that reverses the "effect" of the original function. One important property of the inverse of a function is that whe
From playlist Find the Inverse of a Function
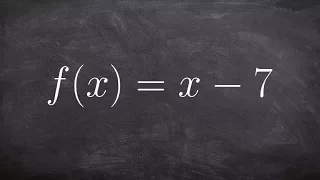
Finding the inverse of a function- Free Online Tutoring
👉 Learn how to find the inverse of a linear function. A linear function is a function whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 1. The inverse of a function is a function that reverses the "effect" of the original function. One important property of the inverse of a function is that whe
From playlist Find the Inverse of a Function

Learn how to identify the inverse of a function and graph
👉 Learn how to find the inverse of a linear function. A linear function is a function whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 1. The inverse of a function is a function that reverses the "effect" of the original function. One important property of the inverse of a function is that whe
From playlist Find the Inverse of a Function

Step by step learn how to write the inverse of a function and determine if a function or not
👉 Learn how to find the inverse of a linear function. A linear function is a function whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 1. The inverse of a function is a function that reverses the "effect" of the original function. One important property of the inverse of a function is that whe
From playlist Find the Inverse of a Function
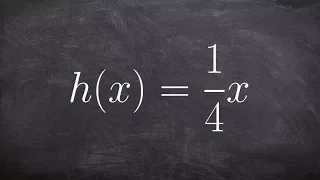
How to find and graph the inverse of a linear function
👉 Learn how to find the inverse of a linear function. A linear function is a function whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 1. The inverse of a function is a function that reverses the "effect" of the original function. One important property of the inverse of a function is that whe
From playlist Find the Inverse of a Function
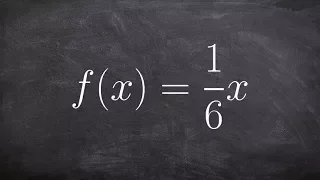
Learn how to find inverse of a function and determine if the inverse is a function or not
👉 Learn how to find the inverse of a linear function. A linear function is a function whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 1. The inverse of a function is a function that reverses the "effect" of the original function. One important property of the inverse of a function is that whe
From playlist Find the Inverse of a Function

Vincent Calvez: Collective movement - course 1
HYBRID EVENT Recorded during the meeting "Mathematical Modeling of Organization in Living Matter" the March 31, 2022 by the Centre International de Rencontres Mathématiques (Marseille, France) Filmmaker: Guillaume Hennenfent Find this video and other talks given by worldwide mathematic
From playlist Partial Differential Equations

Alternatives to Reversing the Order of Integration: Research for Undergraduates
New math research! http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/0020739X.2017.1329559 http://www.tandfonline.com/eprint/YQpJeHUX2PWCuEKuMA83/full This paper presents some critical perspectives regarding pedagogical approaches to the method of reversing the order of integration in double integrals from pr
From playlist Mathematical analysis and applications

Lec 7b - Phys 237: Gravitational Waves with Kip Thorne
Watch the rest of the lectures on http://www.cosmolearning.com/courses/overview-of-gravitational-wave-science-400/ Redistributed with permission. This video is taken from a 2002 Caltech on-line course on "Gravitational Waves", organized and designed by Kip S. Thorne, Mihai Bondarescu and
From playlist Caltech: Gravitational Waves with Kip Thorne - CosmoLearning.com Physics

Reversing order in double integrals
Download the free PDF from http://tinyurl.com/EngMathYT This video shows how to reverse the order of integration in double integrals. Such ideas can simplify the calculations and are seen in university mathematics.
From playlist Mathematics for Finance & Actuarial Studies 2

Topological effects in metals - Moore
Joel Moore November 7, 2015 The recent advances in our understanding of topological states of free-fermion insulators give some valuable concepts and tools for the analysis of metals. The first part of this talk focuses on low-energy electrodynamic responses of simple metals, including th
From playlist Mathematics

Properties of the Time Reversal Operator | Quantum Mechanics
In this video, we will discuss some properties of the time reversal operator in quantum mechanics. We will first talk about physical properties, for instance how certain observables are affected by a time reversal, and then also discuss mathematical properties of anti-unitary operators.
From playlist Quantum Mechanics, Quantum Field Theory

Ellie Baker - Crafts, Math, and the Joy of Turning Things Inside Out - CoM Apr 2021
Infinitely Invertible Infinity paper: http://archive.bridgesmathart.org/2020/bridges2020-83.pdf Invertible Infinity: A Toroidal Fashion Statement paper: http://archive.bridgesmathart.org/2017/bridges2017-49.pdf Trefoil knotted scarf with hidden seams: http://www.ellie-baker.com/shared-st
From playlist Celebration of Mind 2021

Graphing and determining the inverse of a function
👉 Learn how to find the inverse of a linear function. A linear function is a function whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 1. The inverse of a function is a function that reverses the "effect" of the original function. One important property of the inverse of a function is that whe
From playlist Find the Inverse of a Function

Reverse the order in double integrals
Download the free PDF http://tinyurl.com/EngMathYT This video shows how to reverse the order of integration in double integrals. Such ideas can simplify the calculations and are seen in university mathematics.
From playlist Several Variable Calculus / Vector Calculus

