Introduction to Parametric Equations
This video defines a parametric equations and shows how to graph a parametric equation by hand. http://mathispower4u.yolasite.com/
From playlist Parametric Equations

Minimal logic, or minimal calculus, is an intuitionistic and paraconsistent logic, that rejects both the Law of Excluded Middle (LEM) as well as the Principle Of Explosion (Ex Falso Quodlibet, EFQ). https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Minimal_logic https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Principle_of_exp
From playlist Logic

We give a basic construction in paraconsistent logic. If people want to know more about this, I can say a bit more.
From playlist Mathematical Shenanigans

Concavity and Parametric Equations Example
Please Subscribe here, thank you!!! https://goo.gl/JQ8Nys Concavity and Parametric Equations Example. We find the open t-intervals on which the graph of the parametric equations is concave upward and concave downward.
From playlist Calculus
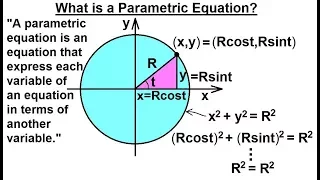
Calculus 2: Parametric Equations (1 of 20) What is a Parametric Equation?
Visit http://ilectureonline.com for more math and science lectures! In this video I will explain what is a parametric equation. A parametric equation is an equation that expresses each variable of an equation in terms of another variable. Next video in the series can be seen at: https://
From playlist CALCULUS 2 CH 17 PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS

What are Non-Classical logics?
Some of the general classes of non-classical logics I touch in this videos are linear logic, relevant logic, modal logic, many-valued logics, minimal logic, paraconsistent logics and so on and so forth. Let me know if I should dive deeping into a certain scene? https://en.wikipedia.org/wi
From playlist Programming

Scalable Privacy-Friendly Client Cloud Computing
Carl Hewitt, Emeritus in the Electrical Engineering and Computer Science department at MIT, talks about Organizations of Restricted Generality (ORGs). ORGs is an architecture providing foundations for the development of privacy-friendly Internet applications by incorporating cloud computin
From playlist Engineering

Entanglement, Black Holes, and Wormholes | An Informal Discussion with Brian Greene
In this year-end wrap up, Brian Greene discusses some of the major advances in science with a focus on breakthroughs in black hole physics and the key roles played by quantum entanglement and wormholes. This program is part of the Big Ideas series, supported by the John Templeton Foundati
From playlist WSU Live Sessions
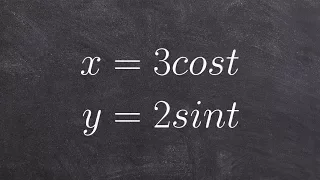
Eliminating the parameter for parametric trigonometric
Learn how to eliminate the parameter in a parametric equation. A parametric equation is a set of equations that express a set of quantities as explicit functions of a number of independent variables, known as parameters. Eliminating the parameter allows us to write parametric equation in r
From playlist Parametric Equations
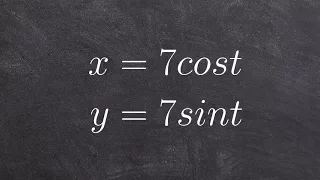
Learn how to eliminate the parameter given sine and cosine of t
Learn how to eliminate the parameter in a parametric equation. A parametric equation is a set of equations that express a set of quantities as explicit functions of a number of independent variables, known as parameters. Eliminating the parameter allows us to write parametric equation in r
From playlist Parametric Equations
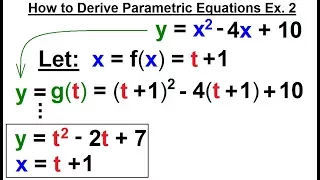
Calculus 2: Parametric Equations (7 of 20) How to Derive Parametric Equations Ex. 2
Visit http://ilectureonline.com for more math and science lectures! In this video I will derive parametric equations. Given x=f(t)=t +1and y=x^2-4x+10 find x(t)=? and y(t)=? Example 2. Next video in the series can be seen at: https://youtu.be/aWy2dpNoYlE
From playlist CALCULUS 2 CH 17 PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS
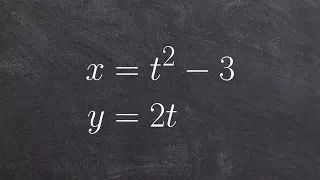
Eliminating the parameter for parametric equations quadratic
Learn how to eliminate the parameter in a parametric equation. A parametric equation is a set of equations that express a set of quantities as explicit functions of a number of independent variables, known as parameters. Eliminating the parameter allows us to write parametric equation in r
From playlist Parametric Equations
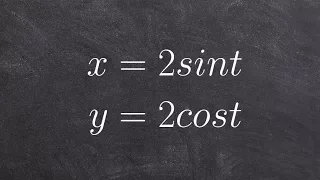
Learn how to eliminate the parameter with trig functions
Learn how to eliminate the parameter in a parametric equation. A parametric equation is a set of equations that express a set of quantities as explicit functions of a number of independent variables, known as parameters. Eliminating the parameter allows us to write parametric equation in r
From playlist Parametric Equations

Logic: The Structure of Reason
As a tool for characterizing rational thought, logic cuts across many philosophical disciplines and lies at the core of mathematics and computer science. Drawing on Aristotle’s Organon, Russell’s Principia Mathematica, and other central works, this program tracks the evolution of logic, be
From playlist Logic & Philosophy of Mathematics

Logic 1 - Overview: Logic Based Models | Stanford CS221: AI (Autumn 2021)
For more information about Stanford's Artificial Intelligence professional and graduate programs visit: https://stanford.io/ai This lecture covers logic-based models: propositional logic, first order logic Applications: theorem proving, verification, reasoning, think in terms of logical f
From playlist Stanford CS221: Artificial Intelligence: Principles and Techniques | Autumn 2021

Excel Statistical Analysis 17: AND, OR, and NOT Logical Tests for COUNTIFS & FILTER Functions
Download Excel File: https://excelisfun.net/files/Ch04-ESA.xlsm pdf notes: https://excelisfun.net/files/Ch04-ESA.pdf Learn about the basics of Logical Tests: AND, OR and NOT. Lean how to count based on logical tests using COUNTIFS, FILTER and ROWS functions. Topics: 1. (00:00) Introduction
From playlist Excel Statistical Analysis for Business Class Playlist of Videos from excelisfun

Inference: A Logical-Philosophical Perspective - Moderated Conversation w/ A.C. Paseau and Gila Sher
Inference: A Logical-Philosophical Perspective. Moderated Conversation with Gila Sher, Department of Philosophy, University of California, San Diego on the talk by Alexander Paseau, Faculty of Philosophy, University of Oxford. The Franke Program in Science and the Humanities Understandi
From playlist Franke Program in Science and the Humanities
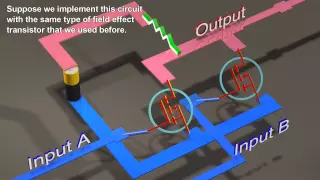
Logic Gates from Transistors: Transistors and Boolean Logic
How to make all the logic gates from a field effect transistor, or from other logic gates.
From playlist Physics

Learn to basics of eliminating the parameter with sine and cosine
Learn how to eliminate the parameter in a parametric equation. A parametric equation is a set of equations that express a set of quantities as explicit functions of a number of independent variables, known as parameters. Eliminating the parameter allows us to write parametric equation in r
From playlist Parametric Equations