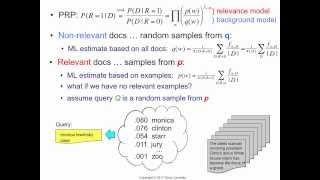
Relevance model 1: Bernoulli sets vs. multinomial urns
[http://bit.ly/RModel] Relevance model is the language model of the relevant class. In this video we look at the difference between the multinomial model (the one used in relevance models) and the multiple-Bernoulli model, which forms the basis for the classical probabilistic models.
From playlist IR18 Relevance Model
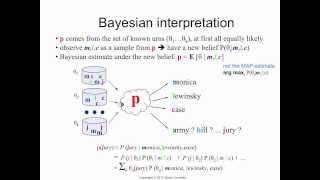
Relevance model 4: Bayesian interpretation
[http://bit.ly/RModel] Another way to interpret the relevance model is via Bayesian estimation: the relevance model could be one of a large set of urns. We know what the urns are, but don't know which one is correct, so we compute the posterior probability for each candidate urn, and combi
From playlist IR18 Relevance Model

Relevance model 5: summary of assumptions
[http://bit.ly/RModel] The relevance model ranking is based on the probability ranking principle (PRP). It uses the background (corpus) model as a language model for the non-relevant class (just like the classical model), but has a novel estimate for the relevance model. The estimate is ba
From playlist IR18 Relevance Model

Evaluation 5: relevance judgments
Relevance judgments indicate which documents are relevant to the information need of a user. They are constructed by trained annotators inspecting a subset of documents (typically pooled across a large number of different retrieval algorithms).
From playlist IR13 Evaluating Search Engines

Logic: The Structure of Reason
As a tool for characterizing rational thought, logic cuts across many philosophical disciplines and lies at the core of mathematics and computer science. Drawing on Aristotle’s Organon, Russell’s Principia Mathematica, and other central works, this program tracks the evolution of logic, be
From playlist Logic & Philosophy of Mathematics

Relevance model 2: the sampling game
[http://bit.ly/RModel] How can we estimate the language model of the relevant class if we have no examples of relevant documents? We play a sampling game as follows. The relevance model is an urn with unknown parameters. We draw several samples from it and observe the query. What is the pr
From playlist IR18 Relevance Model

Relevance model 7: ranking functions
[http://bit.ly/RModel] The probability ranking principle (PRP) seems like the obvious ranking function for relevance models, but when we use it in the form of the odds ratio (as in the classical model), we bias our rankings towards the wrong type of document. A better approach is to use th
From playlist IR18 Relevance Model

Introduction to Predicate Logic
This video introduces predicate logic. mathispower4u.com
From playlist Symbolic Logic and Proofs (Discrete Math)

Wolfram Physics Project: Working Session Tuesday, Mar. 16, 2021 [Bibliographying Combinators]
This is a Wolfram Physics Project working session on bibliographying combinators. Begins at 4:33 Originally livestreamed at: https://twitch.tv/stephen_wolfram Stay up-to-date on this project by visiting our website: http://wolfr.am/physics Check out the announcement post: http://wolfr.am
From playlist Wolfram Physics Project Livestream Archive

Introduction to Philosophy and Logic
Humans are on a quest to understand the world around us. How did this quest begin? What are the tools we use to gather knowledge? How do we know what is possible to know? What do we mean when using words like ethics, ontology, metaphysics, aesthetics, and logic? This series is going to get
From playlist Philosophy/Logic

A talk given by Cora Diamond in 2017 at St. John's College. 00:00 Wittgenstein as a Responsive Philosopher 04:18 Wittgenstein reads Russell 13:24 Wittgenstein & the Spirit of Modernity 20:05 What Next? The Tractatus 30:20 Flaws in the Tractatus 34:23 Wittgenstein’s Diagnosis 41:39 O
From playlist Wittgenstein

Exercises in COMPLEX TRUTH TREES - Logic
In this video in #Logic / #PhilosophicalLogic we do two examples of complex truth trees and then I give general strategies for doing these. The trees here use rules for negation, conjunction, disjunction, the conditional, and the biconditional. 0:00 [Example #1] 4:53 [Example #2] 9:29 [St
From playlist Logic in Philosophy and Mathematics

Fundamentals of Industrial Oil Hydraulics and Pneumatics by Prof. R.N. Maiti,Department of Mechanical Engineering,IIT Kharagpur.For more details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.ac.in
From playlist IIT Kharagpur: Fundamentals of Industrial Oil Hydraulics and Pneumatics (CosmoLearning Mechanical Engineering)

Excel Magic Trick 455: Advanced Filter Macro: Extract Grant Records Under A Cumulative Total
Download Files: https://people.highline.edu/mgirvin/YouTubeExcelIsFun/EMT453-457.xls See how to extract grant records with highest point value and only extract enough records collectively that are under the Total Funding Ceiling: 1.AND function for 2 criteria 2.Running Total Formula w
From playlist Excel Recorded Macros - Excel Macro Recorder
Live CEOing Ep 223: Temporal Logic in Wolfram Language
Watch Stephen Wolfram and teams of developers in a live, working, language design meeting. This episode is about Temporal Logic in the Wolfram Language.
From playlist Behind the Scenes in Real-Life Software Design

O'Reilly Webcast: View Updating: How to Make it Work
Ever since the relational view concept was first invented, view updating has been a contentious issue. Support in today's SQL products is ad hoc and meager at best. The SQL standard is even more impenetrable in this area than it usually is. Even the research literature is weak on this topi
From playlist O'Reilly Webcasts 2

The measurement problem and some mild solutions by Dustin Lazarovici (Lecture - 04)
21 November 2016 to 10 December 2016 VENUE Ramanujan Lecture Hall, ICTS Bangalore Quantum Theory has passed all experimental tests, with impressive accuracy. It applies to light and matter from the smallest scales so far explored, up to the mesoscopic scale. It is also a necessary ingredie
From playlist Fundamental Problems of Quantum Physics

LambdaConf 2015 - Type Theory and its Meaning Explanations Jon Sterling
At the heart of intuitionistic type theory lies an intuitive semantics called the “meaning explanations." Crucially, when meaning explanations are taken as definitive for type theory, the core notion is no longer “proof” but “verification”. We’ll explore how type theories of this sort aris
From playlist LambdaConf 2015

