
Logic: The Structure of Reason
As a tool for characterizing rational thought, logic cuts across many philosophical disciplines and lies at the core of mathematics and computer science. Drawing on Aristotle’s Organon, Russell’s Principia Mathematica, and other central works, this program tracks the evolution of logic, be
From playlist Logic & Philosophy of Mathematics

Geometry - Ch. 2: Reasoning and Proofs (13 of 46) What is Deductive Reasoning?
Visit http://ilectureonline.com for more math and science lectures! In this video I will explain what is deductive reasoning. Sometime known as deductive logic or leading to a deductive conclusion. It is reasoning from one or more statements to reach a logical conclusion. And I will expla
From playlist GEOMETRY CH 2 PROOFS & REASONING

http://www.teachastronomy.com/ Deduction is a way of combining observations or statements made in science logically. Deduction provides a very strong way of connecting observations with a conclusion. Typically we start with premises and combine them to draw conclusions. For example, if
From playlist 01. Fundamentals of Science and Astronomy

Language & Social Ontology (John Searle)
A wonderful talk given by John Searle at the University of Oslo back in 2011 on language and social ontology. He attempts to explain the distinctive features of human civilization. Animals have forms of social organization and communication, but they do not have money, property, government
From playlist Social & Political Philosophy

The Logical Structure of Human Civilization (John Searle)
The distinctive features of human civilization, as opposed to animal societies, are such things as money, property, marriage, government, etc. These are created and partly constituted by linguistic representations. For this reason, they all have logical, propositional structures. John Sear
From playlist Social & Political Philosophy
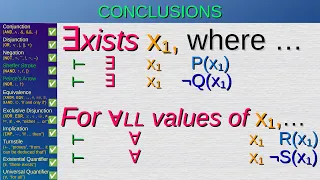
Logic 3: Quantifiers (univ. & exist.), Proofs part 1 — Tutorial 3/4
In this four-part series we explore propositional logic, Karnaugh maps, implications and fallacies, predicate logic, existential and universal quantifiers and finally natural deduction. Become a member: https://youtube.com/Bisqwit/join My links: Twitter: https://twitter.com/RealBisqwit L
From playlist Logic Tutorial

In this lecture, Dr Iain Law (University of Birmingham) introduces the concept of a moral theory and thinks about what distinguishes deontological moral theories from other kinds of moral theories (e.g. virtue ethics, utilitarianism), focusing in particular on: (i) the deontological theory
From playlist Philosophy

SYN124 - The Function of the Verb - Mood and Modality
In this final E-Lecture of the series functional aspects of the verb, Prof. Handke discusses the notions of mood and modality. He exemplifies the rudimentary mood system in PDE and discusses the three modlities, dynamic, deontic, and epistemic in detail.
From playlist VLC201 - The Structure of English

Introduction to Deductive Reasoning
http://www.mathispower4u.yolasite.com
From playlist Introduction to Proof

Natural Deductive Logic: RULES #2 (vI, vE, DN, RAA) - Logic
In this video on #Logic, we learn four more rules for natural deductive proofs. We learn disjunction introduction, disjunction elimination, double negation, and reductio ad absurdum (negation introductions, or proof by contradiction). Then we do two example proofs. #PropositionalLogic #Lo
From playlist Logic in Philosophy and Mathematics

CERIAS Security: Research Challenges in Assured Information Sharing 4/5
Clip 4/5 Speaker: Vipin Swarup · MITRE Assured information sharing has been a "grand challenge" problem of information security for several decades. Currently, there is broad consensus that the state-of-practice of information sharing is inadequate. One primary problem is that people
From playlist The CERIAS Security Seminars 2007

MASSOLIT: Utilitarianism as a Moral Theory
In this lecture, Dr Iain Law (University of Birmingham) provides an introduction to moral theories in general, before thinking in more detail about consequentialism and utilitarianism more specifically. This lecture is part of a larger course on Utilitarianism. The full course can be foun
From playlist Philosophy

Introduction to Mathematical Induction (1 of 2: Two Different kinds of Logic)
More resources available at www.misterwootube.com
From playlist Introduction to Proof by Mathematical Induction

Two Exercises in Natural Deductive Logic: RULES #1 (R, &E, &I, MP, CP) - Logic
We do two more natural deductive proofs using the rules introduced in the last video. They are listed below. 0:00 [Intro] 0:31 [Question #1] 5:27 [Question #2] 9:45 [The Takeaway] Follow along in the Logic playlist: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLDDGPdw7e6AhsNuxXP3D-45Is96L8sdSG
From playlist Logic in Philosophy and Mathematics

Lecture 10 – Grounding | Stanford CS224U: Natural Language Understanding | Spring 2019
For more information about Stanford’s Artificial Intelligence professional and graduate programs, visit: https://stanford.io/ai Professor Christopher Potts & Consulting Assistant Professor Bill MacCartney, Stanford University http://onlinehub.stanford.edu/ Professor Christopher Potts Pr
From playlist Stanford CS224U: Natural Language Understanding | Spring 2019

The Ultimate Guide to Propositional Logic for Discrete Mathematics
This is the ultimate guide to propositional logic in discrete mathematics. We cover propositions, truth tables, connectives, syntax, semantics, logical equivalence, translating english to logic, and even logic inferences and logical deductions. 00:00 Propositions 02:47 Connectives 05:13 W
From playlist Discrete Math 1

Fundamentals of Mathematics - Lecture 33: Dedekind's Definition of Infinite Sets are FInite Sets
https://www.uvm.edu/~tdupuy/logic/Math52-Fall2017.html
From playlist Fundamentals of Mathematics
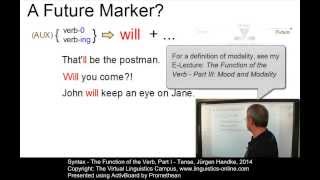
SYN122 - The Function of the Verb - Tense
This first of a series of three E-Lectures deals with the function of the verb in PDE, in particular with the notion of tense. Prof. Handke explains why PDE has only two tenses, the present and the past tense, and how they are used. The discussion why PDE has no future tense concludes this
From playlist VLC201 - The Structure of English

Natural Deductive Logic: DERIVABLE RULES (MT, HS, DS, DeM)
In this video on #Logic we do the proofs for modus tollens (MT), hypothetical syllogism (HS), disjunctive syllogism (DS) and one of the DeMorgan's Laws (DeM) so that we can use them as shortcuts in further proofs. 0:00 [Modus Tollens (MT)] 1:23 [Hypothetical Syllogism (HS)] 3:25 [Disjunct
From playlist Logic in Philosophy and Mathematics