Ordinary differential equations | Differential geometry
Integral curve
In mathematics, an integral curve is a parametric curve that represents a specific solution to an ordinary differential equation or system of equations. (Wikipedia).

Ordinary differential equations | Differential geometry
In mathematics, an integral curve is a parametric curve that represents a specific solution to an ordinary differential equation or system of equations. (Wikipedia).


What is an integral and it's parts
👉 Learn about integration. The integral, also called antiderivative, of a function, is the reverse process of differentiation. Integral of a function can be evaluated as an indefinite integral or as a definite integral. A definite integral is an integral in which the upper and the lower li
From playlist The Integral

Dirichlet Eta Function - Integral Representation
Today, we use an integral to derive one of the integral representations for the Dirichlet eta function. This representation is very similar to the Riemann zeta function, which explains why their respective infinite series definition is quite similar (with the eta function being an alte rna
From playlist Integrals

Find the area enclosed by the two curves using two integrals
Keywords 👉 Learn how to evaluate the integral of a function. The integral, also called antiderivative, of a function, is the reverse process of differentiation. Integral of a function can be evaluated as indefinite integral or as a definite integral. A definite integral is an integral in
From playlist Evaluate Integrals

How to take the integral of tangent
👉 Learn how to evaluate the integral of a function. The integral, also called antiderivative, of a function, is the reverse process of differentiation. Integral of a function can be evaluated as an indefinite integral or as a definite integral. A definite integral is an integral in which t
From playlist The Integral

Apply u substitution to a polynomial
👉 Learn how to evaluate the integral of a function. The integral, also called antiderivative, of a function, is the reverse process of differentiation. Integral of a function can be evaluated as an indefinite integral or as a definite integral. A definite integral is an integral in which t
From playlist The Integral

How to use u substitution to find the indifinite integral
👉 Learn how to evaluate the integral of a function. The integral, also called antiderivative, of a function, is the reverse process of differentiation. Integral of a function can be evaluated as an indefinite integral or as a definite integral. A definite integral is an integral in which t
From playlist The Integral

Find the area enclosed by the two curves using your calculator
Keywords 👉 Learn how to evaluate the integral of a function. The integral, also called antiderivative, of a function, is the reverse process of differentiation. Integral of a function can be evaluated as indefinite integral or as a definite integral. A definite integral is an integral in
From playlist Evaluate Integrals
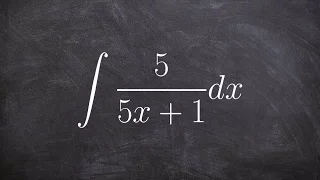
Integrate the a rational expression using logarithms and u substitution
👉 Learn how to evaluate the integral of a function. The integral, also called antiderivative, of a function, is the reverse process of differentiation. Integral of a function can be evaluated as an indefinite integral or as a definite integral. A definite integral is an integral in which t
From playlist The Integral

Find the area enclosed by the two curves
Keywords 👉 Learn how to evaluate the integral of a function. The integral, also called antiderivative, of a function, is the reverse process of differentiation. Integral of a function can be evaluated as indefinite integral or as a definite integral. A definite integral is an integral in
From playlist Evaluate Integrals

Wei Ho, Integral points on elliptic curves
VaNTAGe seminar, on Oct 13, 2020 License: CC-BY-NC-SA. Closed captions provided by Rachana Madhukara.
From playlist Rational points on elliptic curves

Integration over curves (line integrals)
Free ebook http://tinyurl.com/EngMathYT An introduction on how to integrate over curves. The ideas involve integration with respect to the arc length and have important applications, including the mass of thin wires.
From playlist Engineering Mathematics

Part I: Complex Variables, Lec 5: Integrating Complex Functions
Part I: Complex Variables, Lecture 5: Integrating Complex Functions Instructor: Herbert Gross View the complete course: http://ocw.mit.edu/RES18-008F11 License: Creative Commons BY-NC-SA More information at http://ocw.mit.edu/terms More courses at http://ocw.mit.edu
From playlist MIT Calculus Revisited: Calculus of Complex Variables

The Divergence Theorem, a visual explanation
This video talks about the divergence theorem, one of the fundamental theorems of multivariable calculus. The divergence theorem relates a flux integral to a triple integral. Green's Theorem: https://youtu.be/8SwKD5_VL5o Line Integrals: https://youtu.be/dnGDmZynvYY Follow Me! https://i
From playlist Multivariable Calculus

Free ebook http://tinyurl.com/EngMathYT A basic lecture on line integrals involving vector fields. We discuss the motivation for their study and present some examples.
From playlist Engineering Mathematics

Worldwide Calculus: Green's Theorem
Lecture on 'Green's Theorem' from 'Worldwide Multivariable Calculus'. For more lecture videos and $10 digital textbooks, visit www.centerofmath.org.
From playlist Integration and Vector Fields

From playlist Complex Analysis Made Simple

Integration by Parts and Areas under Curves | Algebraic Calculus One | Wild Egg
We start with a purely algebraic Integration by Parts formula, which is a consequence of the Product Rule for Faulhaber Derivatives. Then we apply this to the Fundamental Theorem to get two asymmetric versions of it. Looking at the geometrical significance following a favourite picture o
From playlist Algebraic Calculus One

How to find the integral of an exponential function using u sub
👉 Learn how to evaluate the integral of a function. The integral, also called antiderivative, of a function, is the reverse process of differentiation. Integral of a function can be evaluated as an indefinite integral or as a definite integral. A definite integral is an integral in which t
From playlist The Integral