
Parseval-Plancherel Identity | Normalization in Quantum Mechanics
In this video, we will investigate the Parseval-Plancherel identity, which is named after the French mathematician Marc-Antoine Parseval, and the Swiss mathematician Michel Plancherel. It states that the integral over the absolute square of a function does not change after a Fourier transf
From playlist Quantum Mechanics, Quantum Field Theory
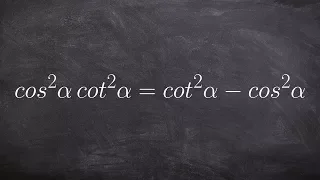
Verify trig identities with multiple identities
👉 Learn how to verify Pythagoras trigonometric identities. A Pythagoras trigonometric identity is a trigonometric identity of the form sin^2 (x) + cos^2 (x) or any of its derivations. To verify trigonometric expression means to verify that the term(s) on the left-hand side of the equality
From playlist Verify Trigonometric Identities
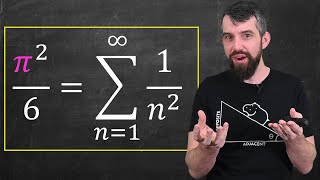
Parseval's Identity, Fourier Series, and Solving this Classic Pi Formula
To celebrate #PiDay we solve the Basel Problem - that the sum of reciprocals of square naturals is pi^2/6 - using techniques from Fourier Analysis, in particular Parseval's Identity, which is a sort of infinite dimensional analog of Pythagoras. Check out my intro playlist on FOURIER SERI
From playlist Fourier
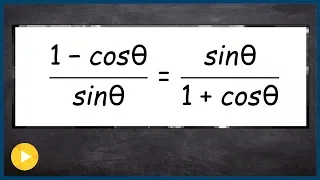
Verify an identity by multiplying by the conjugate
👉 Learn how to verify Pythagoras trigonometric identities. A Pythagoras trigonometric identity is a trigonometric identity of the form sin^2 (x) + cos^2 (x) or any of its derivations. To verify trigonometric expression means to verify that the term(s) on the left-hand side of the equality
From playlist Verify Trigonometric Identities

How to verify a trigonometric identity by using pythagorean identities
👉 Learn how to verify Pythagoras trigonometric identities. A Pythagoras trigonometric identity is a trigonometric identity of the form sin^2 (x) + cos^2 (x) or any of its derivations. To verify trigonometric expression means to verify that the term(s) on the left-hand side of the equality
From playlist Verify Trigonometric Identities

MIT 8.04 Quantum Physics I, Spring 2016 View the complete course: http://ocw.mit.edu/8-04S16 Instructor: Barton Zwiebach License: Creative Commons BY-NC-SA More information at http://ocw.mit.edu/terms More courses at http://ocw.mit.edu
From playlist MIT 8.04 Quantum Physics I, Spring 2016

Fourier series & Parseval's identity
Free ebook http://tinyurl.com/EngMathYT A tutorial on how to calculate Fourier series and how to derive and use Parseval's identity. Many examples are discussed to illustrate the ideas.
From playlist Engineering Mathematics

How to verify a trigonometric identity by factoring
👉 Learn how to verify Pythagoras trigonometric identities. A Pythagoras trigonometric identity is a trigonometric identity of the form sin^2 (x) + cos^2 (x) or any of its derivations. To verify trigonometric expression means to verify that the term(s) on the left-hand side of the equality
From playlist Verify Trigonometric Identities
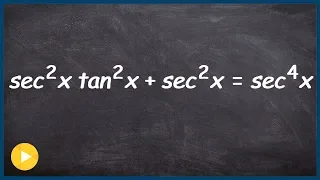
How to verify a trig identity by factoring
👉 Learn how to verify Pythagoras trigonometric identities. A Pythagoras trigonometric identity is a trigonometric identity of the form sin^2 (x) + cos^2 (x) or any of its derivations. To verify trigonometric expression means to verify that the term(s) on the left-hand side of the equality
From playlist Verify Trigonometric Identities
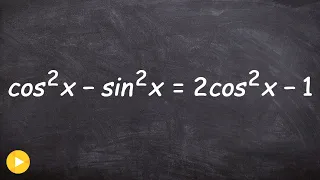
How to verify a trig identity by factoring
👉 Learn how to verify Pythagoras trigonometric identities. A Pythagoras trigonometric identity is a trigonometric identity of the form sin^2 (x) + cos^2 (x) or any of its derivations. To verify trigonometric expression means to verify that the term(s) on the left-hand side of the equality
From playlist Verify Trigonometric Identities

Fourier Series: Example of Parseval's Identity
Differential Equations: Find the Fourier coefficients of the square wave function f(x) = -1 on the interval (-pi, 0), 1 on the interval (0, pi). Then state Parseval's Identity in this case. With this, we show that sum 1/n^2 = pi^2/6.
From playlist Differential Equations

Integral Transforms - Lecture 9: The Fourier Transform in Action. Oxford Maths 2nd Year Lecture
This short course from Sam Howison, all 9 lectures of which we are making available (this is lecture 9), introduces two vital ideas. First, we look at distributions (or generalised functions) and in particular the mathematical representation of a 'point mass' as the Dirac delta function.
From playlist Oxford Mathematics Student Lectures - Integral Transforms
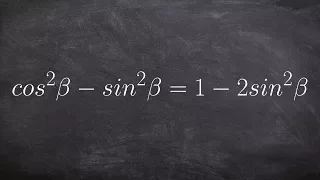
Using the Pythagorean identity to verify an identity
👉 Learn how to verify Pythagoras trigonometric identities. A Pythagoras trigonometric identity is a trigonometric identity of the form sin^2 (x) + cos^2 (x) or any of its derivations. To verify trigonometric expression means to verify that the term(s) on the left-hand side of the equality
From playlist Verify Trigonometric Identities

Lecture 9, Fourier Transform Properties | MIT RES.6.007 Signals and Systems, Spring 2011
Lecture 9, Fourier Transform Properties Instructor: Alan V. Oppenheim View the complete course: http://ocw.mit.edu/RES-6.007S11 License: Creative Commons BY-NC-SA More information at http://ocw.mit.edu/terms More courses at http://ocw.mit.edu
From playlist MIT RES.6.007 Signals and Systems, 1987

Pareto Analysis for Beginners in Excel
Check out the article on Pareto Analysis and download the Excel file here: https://magnimetrics.com/pareto-principle-in-financial-analysis/ Fill our survey for a FREE Benchmark Analysis template! https://forms.gle/A4MLhr7J5rRG1JBi8 If you like this video, drop a comment, give it a thumbs
From playlist Excel Tutorials

Using pythagorean identities to help me verify an identity
👉 Learn how to verify Pythagoras trigonometric identities. A Pythagoras trigonometric identity is a trigonometric identity of the form sin^2 (x) + cos^2 (x) or any of its derivations. To verify trigonometric expression means to verify that the term(s) on the left-hand side of the equality
From playlist Verify Trigonometric Identities

Parseval's theorem is an important result in Fourier analysis that can be used to put guarantees on the accuracy of signal approximation in the Fourier domain. Book Website: http://databookuw.com Book PDF: http://databookuw.com/databook.pdf These lectures follow Chapter 2 from: "Data-D
From playlist Data-Driven Science and Engineering

Here we discuss how to compress images using the FFT. Compression is a cornerstone of the modern digital communication era. Book Website: http://databookuw.com Book PDF: http://databookuw.com/databook.pdf These lectures follow Chapter 2 from: "Data-Driven Science and Engineering: Mac
From playlist Data-Driven Science and Engineering

Linear Algebra: Given an orthonormal basis of R^n, we present a quick method for finding coefficients of linear combination in terms of the basis. We also give an analogue of Parseval's Identity, which relates these coefficients to the squared length of the vector.
From playlist MathDoctorBob: Linear Algebra I: From Linear Equations to Eigenspaces | CosmoLearning.org Mathematics

Verifying trig identities by removing your denominator
👉 Learn how to verify Pythagoras trigonometric identities. A Pythagoras trigonometric identity is a trigonometric identity of the form sin^2 (x) + cos^2 (x) or any of its derivations. To verify trigonometric expression means to verify that the term(s) on the left-hand side of the equality
From playlist Verify Trigonometric Identities