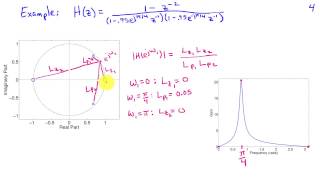
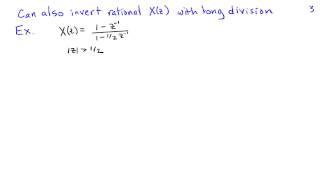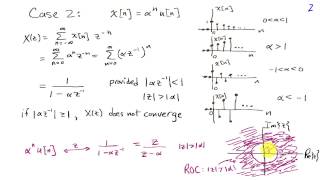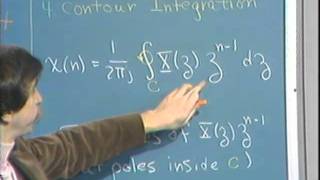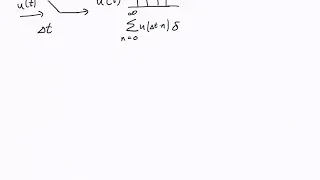Transforms | Laplace transforms
Z-transform
In mathematics and signal processing, the Z-transform converts a discrete-time signal, which is a sequence of real or complex numbers, into a complex frequency-domain (z-domain or z-plane) representation. It can be considered as a discrete-time equivalent of the Laplace transform (s-domain). This similarity is explored in the theory of time-scale calculus. Whereas the continuous-time Fourier transform is evaluated on the Laplace s-domain's imaginary line, the discrete-time Fourier transform is evaluated over the unit circle of the z-domain. What is roughly the s-domain's left half-plane, is now the inside of the complex unit circle; what is the z-domain's outside of the unit circle, roughly corresponds to the right half-plane of the s-domain. One of the means of designing digital filters is to take analog designs, subject them to a bilinear transform which maps them from the s-domain to the z-domain, and then produce the digital filter by inspection, manipulation, or numerical approximation. Such methods tend not to be accurate except in the vicinity of the complex unity, i.e. at low frequencies. (Wikipedia).