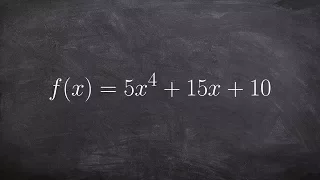Zeros and poles
In complex analysis (a branch of mathematics), a pole is a certain type of singularity of a complex-valued function of a complex variable. In some sense, it is the simplest type of singularity. Technically, a point z0 is a pole of a function f if it is a zero of the function 1/f and 1/f is holomorphic in some neighbourhood of z0 (that is, complex differentiable in a neighbourhood of z0). A function f is meromorphic in an open set U if for every point z of U there is a neighborhood of z in which either f or 1/f is holomorphic. If f is meromorphic in U, then a zero of f is a pole of 1/f, and a pole of f is a zero of 1/f. This induces a duality between zeros and poles, that is fundamental for the study of meromorphic functions. For example, if a function is meromorphic on the whole complex plane plus the point at infinity, then the sum of the multiplicities of its poles equals the sum of the multiplicities of its zeros. (Wikipedia).