
Excel Statistics 36: Trimmed Mean
Download Excel Start File 1: https://people.highline.edu/mgirvin/AllClasses/210M/Content/ch03/Busn210ch03.xls Download Excel Finished File 1: https://people.highline.edu/mgirvin/AllClasses/210M/Content/ch03/Busn210ch03Finished.xls Download Excel Start File 2: https://people.highline.edu/mg
From playlist Excel 2007 Statistics: Charts, Functions, Formulas
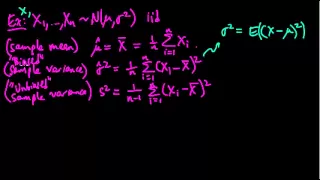
Definition of an estimator. Examples of estimators. Definition of an unbiased estimator.
From playlist Machine Learning

(ML 17.3) Monte Carlo approximation
From playlist Machine Learning

EstimatingRegressionCoeff.7.Unbiased
This video is brought to you by the Quantitative Analysis Institute at Wellesley College. The material is best viewed as part of the online resources that organize the content and include questions for checking understanding: https://www.wellesley.edu/qai/onlineresources
From playlist Estimating Regression Coefficients
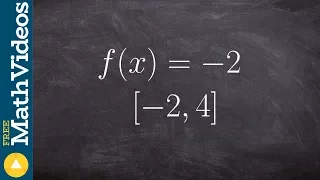
What is the max and min of a horizontal line on a closed interval
👉 Learn how to find the extreme values of a function using the extreme value theorem. The extreme values of a function are the points/intervals where the graph is decreasing, increasing, or has an inflection point. A theorem which guarantees the existence of the maximum and minimum points
From playlist Extreme Value Theorem of Functions

Maximum Likelihood Estimation Examples
http://AllSignalProcessing.com for more great signal processing content, including concept/screenshot files, quizzes, MATLAB and data files. Three examples of applying the maximum likelihood criterion to find an estimator: 1) Mean and variance of an iid Gaussian, 2) Linear signal model in
From playlist Estimation and Detection Theory

DSI | Simultaneous Feature Selection and Outlier Detection Using Mixed-Integer Programming
Simultaneous Feature Selection and Outlier Detection Using Mixed-Integer Programming with Optimality Guarantees Biomedical research is increasingly data rich, with studies comprising ever growing numbers of features. The larger a study, the higher the likelihood that a substantial portion
From playlist DSI Virtual Seminar Series

Gábor Lugosi: High-dimensional mean estimation - lecture 2
Recorded during the meeting "Machine learning and nonparametric statistics" the December 15, 2021 by the Centre International de Rencontres Mathématiques (Marseille, France) Filmmaker: Guillaume Hennenfent Find this video and other talks given by worldwide mathematicians on CIRM's Audio
From playlist Probability and Statistics

Excel 2010 Statistics #29: Means: Weighted, Trimmed, From Grouped Data, Geometric Mean
Download Excel File #1: https://people.highline.edu/mgirvin/AllClasses/210Excel2010/Content/Ch03/Excel2010StatisticsCh03correct.xlsm Download Excel File #2: https://people.highline.edu/mgirvin/AllClasses/210Excel2010/Content/Ch03/Excel2010StatisticsCh03SecondFile.xlsm Download Excel File #
From playlist Excel 2010 Statistics Formulas Functions Charts PivotTables

Least squares method for simple linear regression
In this video I show you how to derive the equations for the coefficients of the simple linear regression line. The least squares method for the simple linear regression line, requires the calculation of the intercept and the slope, commonly written as beta-sub-zero and beta-sub-one. Deriv
From playlist Machine learning

Trimming and Linearization, Part 1: What Is Linearization?
Why go through the trouble of linearizing a model? To paraphrase Richard Feynman, it’s because we know how to solve linear systems. With a linear model we can more easily design a controller, assess stability, and understand the system dynamics. - Learn about linearization for model analys
From playlist Trimming and Linearization

Seminar In the Analysis and Methods of PDE (SIAM PDE): Andrea R. Nahmod
Title: Gibbs measures and propagation of randomness under the flow of nonlinear dispersive PDE Date: Thursday, May 5, 2022, 11:30 am EDT Speaker: Andrea R. Nahmod, University of Massachusetts Amherst The COVID-19 pandemic and consequent social distancing call for online venues of research
From playlist Seminar In the Analysis and Methods of PDE (SIAM PDE)

Fault-tolerant federated and distributed learning
A Google TechTalk, 2020/7/30, presented by Sanmi Koyejo, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign ABSTRACT: Distributed machine learning models are routinely trained using devices that are susceptible to hardware, software, and communication errors, along with other robustness concerns.
From playlist 2020 Google Workshop on Federated Learning and Analytics

Trimming and Linearization, Part 2: The Practical Side of Linearization
With a general understanding of linearization, you might run into a few snags when trying to linearize realistic nonlinear models. These snags can be avoided if you have a more practical understanding of how linearization is accomplished, and that’s what we’ll cover in this video. - Learn
From playlist Trimming and Linearization

How to determine the global max and min from a piecewise function
👉 Learn how to find the extreme values of a function using the extreme value theorem. The extreme values of a function are the points/intervals where the graph is decreasing, increasing, or has an inflection point. A theorem which guarantees the existence of the maximum and minimum points
From playlist Extreme Value Theorem of Functions

Differential Expression in Galaxy
Filmed during an in-person session of the Supercomputing for Everyone Series: De novo Assembly of Transcriptomes at Indiana University, 2018-2019. The complete workshop is free and open to the public compliments of the National Center for Genome Analysis Support (NCGAS). NCGAS is a manag
From playlist De novo Assembly of Transcriptomes

Live CEOing Ep 13: Images, Audio, and Import/Export in the Wolfram Language
Watch Stephen Wolfram and teams of developers in a live, working, language design meeting. This episode is about Images, Audio, and Import/Export in the Wolfram Language.
From playlist Behind the Scenes in Real-Life Software Design

Indexing 13: heuristics for faster search
We discuss the following heuristics for speeding up query execution: caching of search results, binary search (for conjunctions), skip pointers, early termination, top-docs, and prioritised processing.
From playlist IR7 Inverted Indexing

Z Interval [Confidence Interval] for a Proportion
Calculating, understanding, and interpreting a Z Interval [confidence interval] for an unknown population proportion
From playlist Unit 8: Hypothesis Tests & Confidence Intervals for Single Means & for Single Proportions
