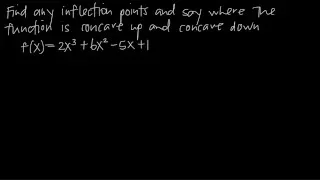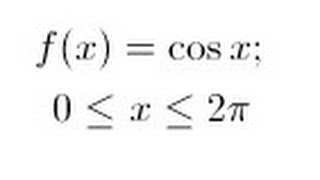Curves | Analytic geometry | Differential geometry | Differential calculus
Inflection point
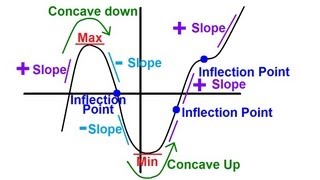
In differential calculus and differential geometry, an inflection point, point of inflection, flex, or inflection (British English: inflexion) is a point on a smooth plane curve at which the curvature changes sign. In particular, in the case of the graph of a function, it is a point where the function changes from being concave (concave downward) to convex (concave upward), or vice versa. For the graph of a function of differentiability class C2 (f, its first derivative f', and its second derivative f'', exist and are continuous), the condition f'' = 0 can also be used to find an inflection point since a point of f'' = 0 must be passed to change f'' from a positive value (concave upward) to a negative value (concave downward) or vice versa as f'' is continuous; an inflection point of the curve is where f'' = 0 and changes its sign at the point (from positive to negative or from negative to positive). A point where the second derivative vanishes but does not change its sign is sometimes called a point of undulation or undulation point. In algebraic geometry an inflection point is defined slightly more generally, as a regular point where the tangent meets the curve to order at least 3, and an undulation point or hyperflex is defined as a point where the tangent meets the curve to order at least 4. (Wikipedia).