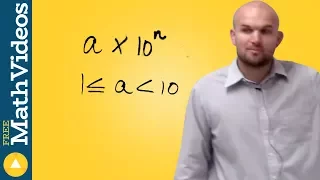Elementary arithmetic | Numbers | Mathematical terminology
Sign (mathematics)
In mathematics, the sign of a real number is its property of being either positive, negative, or zero. Depending on local conventions, zero may be considered as being neither positive nor negative (having no sign or a unique third sign), or it may be considered both positive and negative (having both signs). Whenever not specifically mentioned, this article adheres to the first convention. In some contexts, it makes sense to consider a signed zero (such as floating-point representations of real numbers within computers). In mathematics and physics, the phrase "change of sign" is associated with the generation of the additive inverse (negation, or multiplication by −1) of any object that allows for this construction, and is not restricted to real numbers. It applies among other objects to vectors, matrices, and complex numbers, which are not prescribed to be only either positive, negative, or zero. The word "sign" is also often used to indicate other binary aspects of mathematical objects that resemble positivity and negativity, such as odd and even (sign of a permutation), sense of orientation or rotation (cw/ccw), one sided limits, and other concepts described in below. (Wikipedia).