
Homomorphisms in abstract algebra
In this video we add some more definition to our toolbox before we go any further in our study into group theory and abstract algebra. The definition at hand is the homomorphism. A homomorphism is a function that maps the elements for one group to another whilst maintaining their structu
From playlist Abstract algebra

Ring Theory: We define ring homomorphisms, ring isomorphisms, and kernels. These will be used to draw an analogue to the connections in group theory between group homomorphisms, normal subgroups, and quotient groups.
From playlist Abstract Algebra

Abstract Algebra | Ring homomorphisms
We give the definition of a ring homomorphism as well as some examples. http://www.michael-penn.net https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Michael_Penn5 http://www.randolphcollege.edu/mathematics/
From playlist Abstract Algebra

Homomorphisms in abstract algebra examples
Yesterday we took a look at the definition of a homomorphism. In today's lecture I want to show you a couple of example of homomorphisms. One example gives us a group, but I take the time to prove that it is a group just to remind ourselves of the properties of a group. In this video th
From playlist Abstract algebra
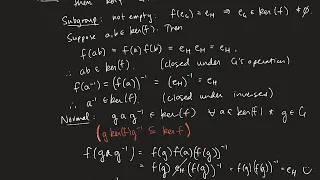
Group Homomorphisms and the big Homomorphism Theorem
This project was created with Explain Everything™ Interactive Whiteboard for iPad.
From playlist Modern Algebra

Group Homomorphisms - Abstract Algebra
A group homomorphism is a function between two groups that identifies similarities between them. This essential tool in abstract algebra lets you find two groups which are identical (but may not appear to be), only similar, or completely different from one another. Homomorphisms will be
From playlist Abstract Algebra

Visual Group Theory, Lecture 7.3: Ring homomorphisms
Visual Group Theory, Lecture 7.3: Ring homomorphisms A ring homomorphism is a structure preserving map between rings, which means that f(x+y)=f(x)+f(y) and f(xy)=f(x)f(y) both must hold. The kernel is always a two-sided ideal. There are four isomorphism theorems for rings, which are compl
From playlist Visual Group Theory

Schemes 10: Morphisms of affine schemes
This lecture is part of an online algebraic geometry course on schemes, based on chapter II of "Algebraic geometry" by Hartshorne. We try to define morphisms of schemes. The obvious definition as morphisms of ringed spaces fails as we show in an example. Instead we have to use the more su
From playlist Algebraic geometry II: Schemes

Isomorphisms in abstract algebra
In this video I take a look at an example of a homomorphism that is both onto and one-to-one, i.e both surjective and injection, which makes it a bijection. Such a homomorphism is termed an isomorphism. Through the example, I review the construction of Cayley's tables for integers mod 4
From playlist Abstract algebra

From playlist Abstract Algebra 2

Schemes 23: Valuations and separation
This lecture is part of an online algebraic geometry course on schemes, based on chapter II of "Algebraic geometry" by Hartshorne.. We state a condition for morphisms of schemes to be separated in therms of discrete valuation rings, and apply this to the line with two origins and the proje
From playlist Algebraic geometry II: Schemes

Abstract Algebra | Properties and examples of ring homomorphisms.
We present some important properties of ring homomorphisms and give some examples. For instance we prove that 2Z and 3Z are isomorphic as groups but not rings. http://www.michael-penn.net https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Michael_Penn5 http://www.randolphcollege.edu/mathematics/
From playlist Abstract Algebra

Ring Homomorphisms: I an Ideal in R implies Φ(I) is an Ideal in S
Ring Homomorphisms and more Ring homomorphisms. In this video I'm talking about mapping and ideal in one ring makes an ideal in another ring. (if the map is onto) I hope you learn something, have a great day! Some of the links below are affiliate links. As an Amazon Associate I earn from
From playlist Abstract Algebra

Charles Rezk: Elliptic cohomology and elliptic curves (Part 2)
The lecture was held within the framework of the Felix Klein Lectures at Hausdorff Center for Mathematics on the 3. June 2015
From playlist HIM Lectures 2015
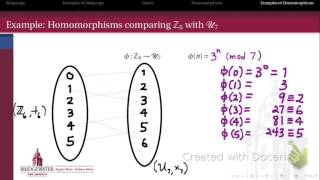
302.3A: Review of Homomorphisms
A visit to the homomorphism "zoo," including definitions of mono-, epi-, iso-, endo-, and automorphisms.
From playlist Modern Algebra - Chapter 17 (group homomorphisms)
