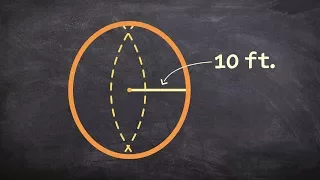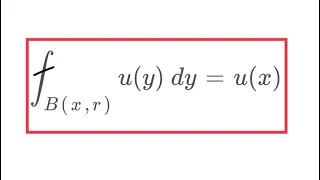Multi-dimensional geometry | Spheres
N-sphere
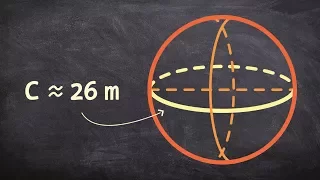
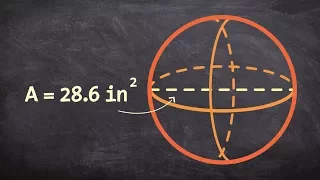
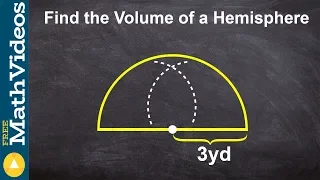
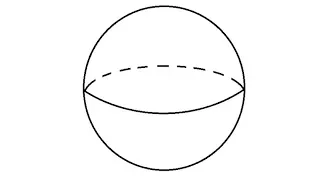
In mathematics, an n-sphere or a hypersphere is a topological space that is homeomorphic to a standard n-sphere, which is the set of points in (n + 1)-dimensional Euclidean space that are situated at a constant distance r from a fixed point, called the center. It is the generalization of an ordinary sphere in the ordinary three-dimensional space. The "radius" of a sphere is the constant distance of its points to the center. When the sphere has unit radius, it is usual to call it the unit n-sphere or simply the n-sphere for brevity. In terms of the standard norm, the n-sphere is defined as and an n-sphere of radius r can be defined as The dimension of n-sphere is n, and must not be confused with the dimension (n + 1) of the Euclidean space in which it is naturally embedded. An n-sphere is the surface or boundary of an (n + 1)-dimensional ball. In particular: * the pair of points at the ends of a (one-dimensional) line segment is a 0-sphere, * a circle, which is the one-dimensional circumference of a (two-dimensional) disk, is a 1-sphere, * the two-dimensional surface of a three-dimensional ball is a 2-sphere, often simply called a sphere, * the three-dimensional boundary of a (four-dimensional) 4-ball is a 3-sphere, * the (n – 1)-dimensional boundary of a (n-dimensional) n-ball is an (n – 1)-sphere. For n ≥ 2, the n-spheres that are differential manifolds can be characterized (up to a diffeomorphism) as the simply connected n-dimensional manifolds of constant, positive curvature. The n-spheres admit several other topological descriptions: for example, they can be constructed by gluing two n-dimensional Euclidean spaces together, by identifying the boundary of an n-cube with a point, or (inductively) by forming the suspension of an (n − 1)-sphere. The 1-sphere is the 1-manifold that is a circle, which is not simply connected. The 0-sphere is the 0-manifold, which is not even connected, consisting of two points. (Wikipedia).