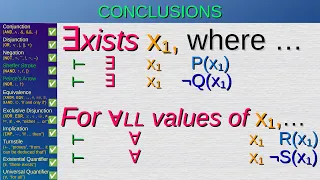Mathematical logic | Modal logic
Modal logic
Modal logic is a collection of formal systems developed to represent statements about necessity and possibility. It plays a major role in philosophy of language, epistemology, metaphysics, and natural language semantics. Modal logics extend other systems by adding unary operators and , representing possibility and necessity respectively. For instance the modal formula can be read as "possibly " while can be read as "necessarily ". Modal logics can be used to represent different phenomena depending on what kind of necessity and possibility is under consideration. When is used to represent epistemic necessity, states that is epistemically necessary, or in other words that it is known. When is used to represent deontic necessity, states that is a moral or legal obligation. In the standard relational semantics for modal logic, formulas are assigned truth values relative to a possible world. A formula's truth value at one possible world can depend on the truth values of other formulas at other accessible possible worlds. In particular, is true at a world if is true at some accessible possible world, while is true at a world if is true at every accessible possible world. A variety of proof systems exist which are sound and complete with respect to the semantics one gets by restricting the accessibility relation. For instance, the deontic modal logic D is sound and complete if one requires the accessibility relation to be serial. While the intuition behind modal logic dates back to antiquity, the first modal axiomatic systems were developed by C. I. Lewis in 1912. The now-standard relational semantics emerged in the mid twentieth century from work by Arthur Prior, Jaakko Hintikka, and Saul Kripke. Recent developments include alternative topological semantics such as neighborhood semantics as well as applications of the relational semantics beyond its original philosophical motivation. Such applications include game theory, moral and legal theory, web design, multiverse-based set theory, and social epistemology. (Wikipedia).