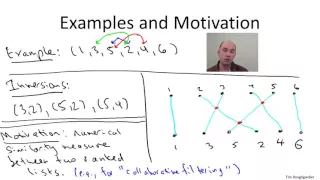
(New Version Available) Inverse Functions
New Version: https://youtu.be/q6y0ToEhT1E Define an inverse function. Determine if a function as an inverse function. Determine inverse functions. http://mathispower4u.wordpress.com/
From playlist Exponential and Logarithmic Expressions and Equations
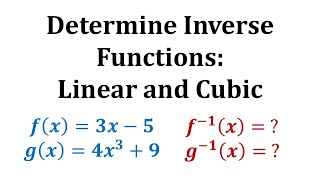
Ex 1: Find the Inverse of a Function
This video provides two examples of how to determine the inverse function of a one-to-one function. A graph is used to verify the inverse function was found correctly. Library: http://mathispower4u.com Search: http://mathispower4u.wordpress.com
From playlist Determining Inverse Functions
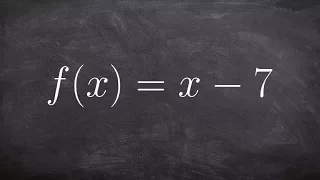
Finding the inverse of a function- Free Online Tutoring
👉 Learn how to find the inverse of a linear function. A linear function is a function whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 1. The inverse of a function is a function that reverses the "effect" of the original function. One important property of the inverse of a function is that whe
From playlist Find the Inverse of a Function

Math 030 Calculus I 031315: Inverse Functions and Differentiation
Inverse functions. Examples of determining the inverse. Relation between the graphs of a function and its inverse. One-to-one functions. Restricting the domain of a function so that it is invertible. Differentiability of inverse functions; relation between derivatives of function and
From playlist Course 2: Calculus I
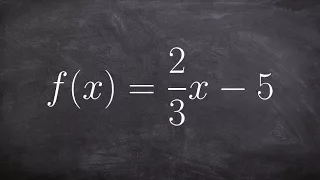
Use the inverse of a function to determine the domain and range
👉 Learn how to find the inverse of a linear function. A linear function is a function whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 1. The inverse of a function is a function that reverses the "effect" of the original function. One important property of the inverse of a function is that whe
From playlist Find the Inverse of a Function
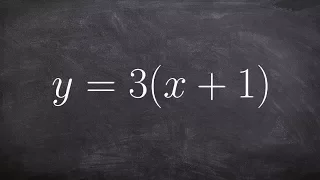
Learn step by step how to find the inverse of an equation, then determine if a function or not
👉 Learn how to find the inverse of a linear function. A linear function is a function whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 1. The inverse of a function is a function that reverses the "effect" of the original function. One important property of the inverse of a function is that whe
From playlist Find the Inverse of a Function
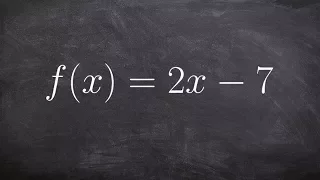
Learn how to find the inverse of a linear equation step by step
👉 Learn how to find the inverse of a linear function. A linear function is a function whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 1. The inverse of a function is a function that reverses the "effect" of the original function. One important property of the inverse of a function is that whe
From playlist Find the Inverse of a Function
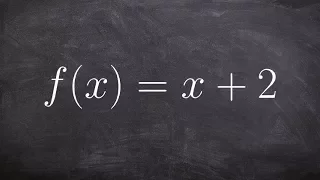
How does the graph of a function compare to it's inverse
👉 Learn how to find the inverse of a linear function. A linear function is a function whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 1. The inverse of a function is a function that reverses the "effect" of the original function. One important property of the inverse of a function is that whe
From playlist Find the Inverse of a Function

Learn how to identify the inverse of a function and graph
👉 Learn how to find the inverse of a linear function. A linear function is a function whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 1. The inverse of a function is a function that reverses the "effect" of the original function. One important property of the inverse of a function is that whe
From playlist Find the Inverse of a Function
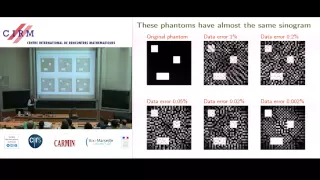
Samuli Siltanen: Reconstruction methods for ill-posed inverse problems - Part 1
Find this video and other talks given by worldwide mathematicians on CIRM's Audiovisual Mathematics Library: http://library.cirm-math.fr. And discover all its functionalities: - Chapter markers and keywords to watch the parts of your choice in the video - Videos enriched with abstracts, b
From playlist Partial Differential Equations

Data-driven regularisation for solving inverse problems - Carola-Bibiane Schönlieb, Turing/Cambridge
In this talk we discuss the idea of data- driven regularisers for inverse imaging problems. We are in particular interested in the combination of model-based and purely data-driven image processing approaches. In this context we will make a journey from “shallow” learning for computing opt
From playlist Statistics and computation

Lec-15 Solution of a System of Linear Algebraic Equations-Part-5
Lecture series on Numerical Methods and Computation by Prof.S.R.K.Iyengar, Department of Mathematics, IIT Delhi. For more details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.iitm.ac.in
From playlist Core - Numerical Methods and Computation

Inverse Trig Functions || 9 Examples
In this video you will see 9 examples of trigonometry problems involving the inverse trig functions. I hope this helps someone. If you enjoyed this video please consider liking, sharing, and subscribing. Udemy Courses Via My Website: https://mathsorcerer.com Free Homework Help : https:
From playlist Math Tutorials

Qin Li - Multiscale inverse problem, from Schroedinger to Newton to Boltzmann - IPAM at UCLA
Recorded 11 April 2022. Qin Li of the University of Wisconsin-Madison, Mathematics, presents "Multiscale inverse problem, from Schroedinger to Newton to Boltzmann" at IPAM's Model Reduction in Quantum Mechanics Workshop. Abstract: Inverse problems are ubiquitous. People probe the media wit
From playlist 2022 Model Reduction in Quantum Mechanics Workshop
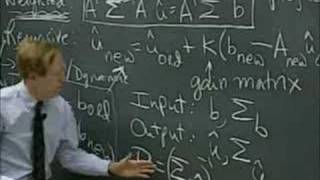
Lec 15 | MIT 18.085 Computational Science and Engineering I
Numerical methods in estimation: recursive least squares and covariance matrix A more recent version of this course is available at: http://ocw.mit.edu/18-085f08 License: Creative Commons BY-NC-SA More information at http://ocw.mit.edu/terms More courses at http://ocw.mit.edu
From playlist MIT 18.085 Computational Science & Engineering I, Fall 2007

Matti Lassas: "New deep neural networks solving non-linear inverse problems"
High Dimensional Hamilton-Jacobi PDEs 2020 Workshop II: PDE and Inverse Problem Methods in Machine Learning "New deep neural networks solving non-linear inverse problems" Matti Lassas - University of Helsinki Abstract: We consider a new type of deep neural network developed to solve nonl
From playlist High Dimensional Hamilton-Jacobi PDEs 2020
Inverse functions -- College Algebra
This lecture is on College Algebra. It follows the introductory part of the book Calculus Illustrated by Peter Saveliev. The text of the book can be found at http://calculus123.com.
From playlist College Algebra

9. Four Ways to Solve Least Squares Problems
MIT 18.065 Matrix Methods in Data Analysis, Signal Processing, and Machine Learning, Spring 2018 Instructor: Gilbert Strang View the complete course: https://ocw.mit.edu/18-065S18 YouTube Playlist: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLUl4u3cNGP63oMNUHXqIUcrkS2PivhN3k In this lecture, P
From playlist MIT 18.065 Matrix Methods in Data Analysis, Signal Processing, and Machine Learning, Spring 2018

Graphing and determining the inverse of a function
👉 Learn how to find the inverse of a linear function. A linear function is a function whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 1. The inverse of a function is a function that reverses the "effect" of the original function. One important property of the inverse of a function is that whe
From playlist Find the Inverse of a Function