
A set might contain many inverse elements under some binary operation. To have such an element, this set must also contain an identity element under the binary operation in question. An element is an inverse element of another element in a set if performing the binary operation between t
From playlist Abstract algebra

Write the inverse of a linear equations
👉 Learn how to find the inverse of a linear function. A linear function is a function whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 1. The inverse of a function is a function that reverses the "effect" of the original function. One important property of the inverse of a function is that whe
From playlist Find the Inverse of a Function

👉 Learn how to find the inverse of a linear function. A linear function is a function whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 1. The inverse of a function is a function that reverses the "effect" of the original function. One important property of the inverse of a function is that whe
From playlist Find the Inverse of a Function

What does the inverse mean when finding the inverse of an equation
👉 Learn how to find the inverse of a linear function. A linear function is a function whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 1. The inverse of a function is a function that reverses the "effect" of the original function. One important property of the inverse of a function is that whe
From playlist Find the Inverse of a Function
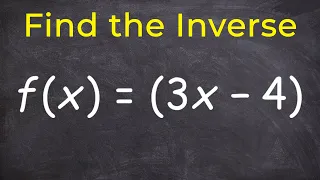
Finding the inverse of a function
👉 Learn how to find the inverse of a linear function. A linear function is a function whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 1. The inverse of a function is a function that reverses the "effect" of the original function. One important property of the inverse of a function is that whe
From playlist Find the Inverse of a Function
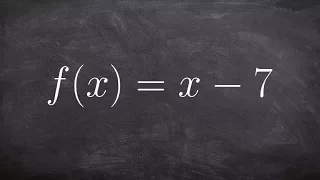
Finding the inverse of a function- Free Online Tutoring
👉 Learn how to find the inverse of a linear function. A linear function is a function whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 1. The inverse of a function is a function that reverses the "effect" of the original function. One important property of the inverse of a function is that whe
From playlist Find the Inverse of a Function

Inverse of a linear equation with fraction
👉 Learn how to find the inverse of a linear function. A linear function is a function whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 1. The inverse of a function is a function that reverses the "effect" of the original function. One important property of the inverse of a function is that whe
From playlist Find the Inverse of a Function

What is the inverse of a function and how do you find it
👉 Learn how to find the inverse of a linear function. A linear function is a function whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 1. The inverse of a function is a function that reverses the "effect" of the original function. One important property of the inverse of a function is that whe
From playlist Find the Inverse of a Function
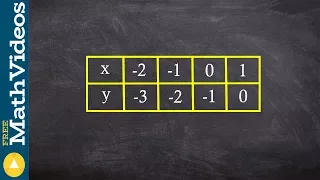
Given a table of values for a function, find the points for the inverse of the function
👉 Learn how to find the inverse of a function. The inverse of a function is a function that reverses the "effect" of the original function. One important property of the inverse of a function is that when the inverse of a function is made the argument (input) of a function, the result is x
From playlist Find the Inverse of a Function

Researchers Use Group Theory to Speed Up Algorithms — Introduction to Groups
This is the most information-dense introduction to group theory you'll see on this website. If you're a computer scientist like me and have always wondered what group theory is useful for and why it even exists and furthermore don't want to bother spending hours learning the basics, this i
From playlist Summer of Math Exposition 2 videos

301.2B Basic Properties of Groups
A group in abstract algebra is a relatively simple structure — but in this video we see how that simple structure enables us to do a lot of what we understand as basic algebra, such as solving equations via cancellation, and having unique identity and inverses.
From playlist Modern Algebra
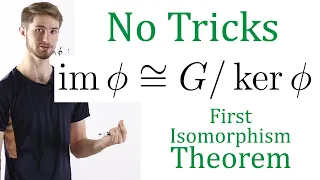
A Natural Proof of the First Isomorphism Theorem (Group Theory)
The first isomorphism theorem is one of the most important theorems in group theory, but the standard proof may seem artificial, like every step of the proof is set up knowing that we're trying to create an isomorphism. In this video, we show an alternate proof with no such tricks using th
From playlist Group Theory

EDIT: At 3:20, nonzero elements have order 3, not 2. Abstract Algebra: We consider the group Aut(G) of automorphisms of G, the isomorphisms from G to itself. We show that the inner automorphisms of G, induced by conjugation, form a normal subgroup Inn(G) of Aut(G), and that Inn(G) is i
From playlist Abstract Algebra

Lec-15 Solution of a System of Linear Algebraic Equations-Part-5
Lecture series on Numerical Methods and Computation by Prof.S.R.K.Iyengar, Department of Mathematics, IIT Delhi. For more details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.iitm.ac.in
From playlist Core - Numerical Methods and Computation

Examples With Cosets -- Abstract Algebra Examples 9
⭐Support the channel⭐ Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/michaelpennmath Merch: https://teespring.com/stores/michael-penn-math My amazon shop: https://www.amazon.com/shop/michaelpenn 🟢 Discord: https://discord.gg/Ta6PTGtKBm ⭐my other channels⭐ Main Channel: https://www.youtube.
From playlist Abstract Algebra

General Results on Groups -- Abstract Algebra Examples 6
⭐Support the channel⭐ Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/michaelpennmath Merch: https://teespring.com/stores/michael-penn-math My amazon shop: https://www.amazon.com/shop/michaelpenn 🟢 Discord: https://discord.gg/Ta6PTGtKBm ⭐my other channels⭐ Main Channel: https://www.youtube.
From playlist Abstract Algebra
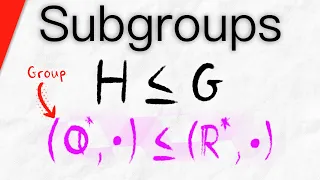
All About Subgroups | Abstract Algebra
We introduce subgroups, the definition of subgroup, examples and non-examples of subgroups, and we prove that subgroups are groups. We also do an example proving a subset is a subgroup. If G is a group and H is a nonempty subset of G, we say H is a subgroup of G if H is closed with respect
From playlist Abstract Algebra

A Simple Group Element Inverse Proof | Abstract Algebra
We prove a simple result about inverse elements in groups while gunshots rattle off in the distance of the forest. If a and b are elements of a group G with identity e such that ab = e, then we can conclude that a=b^-1 and b=a^-1. So, if two elements combine to form the identity, we can co
From playlist Abstract Algebra
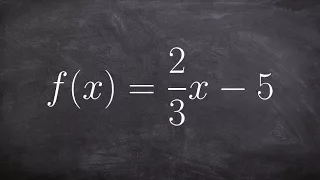
Use the inverse of a function to determine the domain and range
👉 Learn how to find the inverse of a linear function. A linear function is a function whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 1. The inverse of a function is a function that reverses the "effect" of the original function. One important property of the inverse of a function is that whe
From playlist Find the Inverse of a Function
