
ES is a complement to value at risk (VaR). ES is the average loss in the tail; i.e., the expected loss *conditional* on the loss exceeding the VaR quantile. For more financial risk videos, visit our website! http://www.bionicturtle.com
From playlist Tail

Expected shortfall (ES, FRM T5-02)
In this video, I'm going to show you exactly how we calculate expected shortfall under basic historical simulation. Expected shortfall is both desirable and timely. It's desirable because it is coherent, satisfies all four conditions of coherence, including subadditivity, whereas var does
From playlist Market Risk (FRM Topic 5)

Expected shortfall: approximating continuous, with code (ES continous, FRM T5-03)
In my previous video, I showed you how we retrieve expected shortfall under the simplest possible discrete case. That was a simple historical simulation, but that was discrete. In this video, I'm going to review expected shortfall when the distribution is continuous. Specifically, I will u
From playlist Market Risk (FRM Topic 5)

Risk Management Lesson 5A: Value at Risk
In this first part of Lesson 5, we discuss Value-at-Risk (VaR). Topics: - Definition of VaR - Loss distribution and confidence level - The normal VaR
From playlist Risk Management

Overfitting 3: confidence interval for error
[http://bit.ly/overfit] The error on the test set is an approximation of the true future error. How close is it? We show how to compute a confidence interval [a,b] such that the error of our classifier in the future is between a and b (with high probability, and under the assumption that f
From playlist Overfitting

Discrete Population Expected Value applications
Discrete Population Expected Value applications
From playlist Exam 1 material

From playlist a. Numbers and Measurement
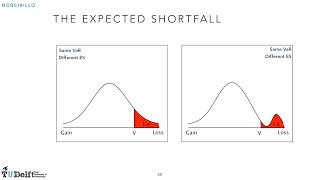
Risk Management 5B: Value at Risk (continued) and Expected Shortfall
This is the second part of Lesson 5. Topics: - The VaR for empirical distributions - The Expected Shortfall - Coherence of VaR and ES
From playlist Risk Management

How to calculate margin of error and standard deviation
In this tutorial I show the relationship standard deviation and margin of error. I calculate margin of error and confidence intervals with different standard deviations. Playlist on Confidence Intervals http://www.youtube.com/course?list=EC36B51DB57E3A3E8E Like us on: http://www.facebook
From playlist Confidence Intervals

QRM L2-2: Value-at-Risk and Expected Shortfall
Welcome to Quantitative Risk Management (QRM). In this video we briefly introduce VaR and ES. Please notice that many concepts are given for granted, and, in case you need more basic details, I refer you to extra videos (check the links appearing on screen). We shall see that ES is always
From playlist Quantitative Risk Management

QRM 9-1: Market risk and historical simulation
Welcome to Quantitative Risk Management (QRM). It is time to introduce market risk, and to start considering how we can assess and hedge it according to the Basel regulations. We will see that VaR and ES are the main quantities we will use, but we know that they need a loss distribution t
From playlist Quantitative Risk Management

Welcome to Quantitative Risk Management (QRM). In this lesson, we play with R to deal with VaR and ES. We show how to compute them empirically, but also in the case of normality. We then show that normality tends to underestimate tail risk, as observable in actual financial data. The pdf
From playlist Quantitative Risk Management

Lars Popken: Minimum capital requirements for market risk under FRTB
A live recording at RiskMinds International with Lars Popken, Global Head of Risk Methodology at Deutsche Bank. Find out more at https://goo.gl/KVtbtC.
From playlist RiskMinds Live 2016

Risk Management Lesson 9A: Historical Simulation for Market Risk
In this first part of Lesson 9, we deal with Historical Simulation for Market Risk under the Basel Framework. Topics: - Market Risk: basic definition - Historical Simulation, how does it work? - The Procyclicality of VaR - Example of Historical Simulation Link to the Excel file about His
From playlist Risk Management

Dependence Uncertainty and Risk - Prof. Paul Embrechts
Abstract I will frame this talk in the context of what I refer to as the First and Second Fundamental Theorem of Quantitative Risk Management (1&2-FTQRM). An alternative subtitle for 1-FTQRM would be "Mathematical Utopia", for 2-FTQRM it would be "Wall Street Reality". I will mainly conce
From playlist Uncertainty and Risk

How to find expected value by hand and in Excel using SUMPRODUCT.
From playlist Basic Statistics (Descriptive Statistics)