
Unexpected loss (UL) of a portfolio of credit assets
The unexpected loss (UL) of a portfolio of credit assets incorporate individual asset ULs and pairwise default correlations
From playlist Credit Risk: Introduction

FRM: Risk contribution of credit to portfolio unexpected loss
Risk contribution is analogous to systematic risk in single-factor (capital asset pricing model): as Ong says, it is a measure of the “undiversified risk of an asset in the portfolio. It is the amount of credit risk which cannot be diversified away by placing the asset in the portfolio.” F
From playlist Credit Risk: Introduction

Liquidity support in a securitization
Internal liquidity support includes: Liability design (e.g., time tranching) or a Liquidity Reserve. External support includes: Lines of credit (LOC) and asset swaps
From playlist Credit Risk: Securitization

A review of the method used in the first building block of CreditMetrics, a ratings-based credit risk portfolio model. You can find the spreadsheet here: http://trtl.bz/2si88RS. For more financial risk videos, visit our website! http://www.bionicturtle.com
From playlist Credit Risk: Portfolio Risk

Cyber risk quantification: What do you need to consider?
Gil Hazaz, VP Sales – Enterprise, KOVRR
From playlist RiskMinds 2021

FRM: Intro credit risk: expected loan return
The expected return on a loan adjusts for default risk. If p = probability of repayment, then 1-p = probability of non-repayment. The expected non-repayment, E[loan amount*(1-p)], is an expected loss (EL) covered by loan loss provisions (a contra-asset account). A "cost of doing business"
From playlist Credit Risk: Introduction

Risk Management Lesson 5A: Value at Risk
In this first part of Lesson 5, we discuss Value-at-Risk (VaR). Topics: - Definition of VaR - Loss distribution and confidence level - The normal VaR
From playlist Risk Management

QRM L1-1: The Definition of Risk
Welcome to Quantitative Risk Management (QRM). In this first class, we define what risk if for us. We will discuss the basic characteristics of risk, underlining some important facts, like its subjectivity, and the impossibility of separating payoffs and probabilities. Understanding the d
From playlist Quantitative Risk Management
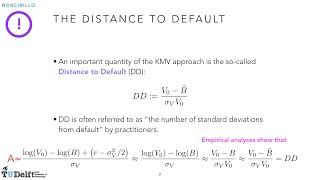
Risk Management Lesson 8A: Industrial Models for Credit Risk
In this first part of Lesson 8, we deal with two important credit risk models developed by the industry. Topics: - Moody's KMV - CreditMetrics (J.P. Morgan & Co.)
From playlist Risk Management

Financial Derivatives - Class 9 - Credit Derivatives
A credit derivative is a type of financial instrument designed to separate and transfer the credit risk or the risk of an event of default of a corporate or sovereign borrower, transferring it to an entity other than the lender or debtholder. Usually these contracts are traded pursuant to
From playlist Full Financial Derivatives Lectures

In Todays video we will learn all about Credit Derivatives including Asset Backed Securities (ABS) Credit Default Swaps (CDS) and Collateralized Debt Obligations (CDO's) These classes are all based on the book Derivatives For The Trading Floor, available on Amazon at this link. https://am
From playlist Credit Derivatives

Risk Management Lesson 6B: Intro Credit Risk, The Standardized Approach and the IRBs.
Second part of Lesson 6. Topics: - Credit Risk (CR) as portmanteau risk - Credit Risk in the Basel Framework - The Standardized approach to CR - The Basics of IRBs
From playlist Risk Management

What is financial risk? FRM Foundations (T1-01)
Financial risk includes market risk, credit risk, operational risk, liquidity risk, and investment risk. 💡 Discuss this video here in our FRM forum: https://trtl.bz/2ywkLLE 👉 Subscribe here https://www.youtube.com/c/bionicturtl... to be notified of future tutorials on expert finance and
From playlist Risk Foundations (FRM Topic 1)

2012 FRM Credit Risk Measurement & Management T6.b
This is a sample of our 2012 FRM Credit Risk Measurement & Management T6.b video tutorials. You may view our products here: https://www.bionicturtle.com/products/financial-risk-management/ The Bionic Turtle program is the most effective and affordable preparation aid for the Financial Ri
From playlist FRM
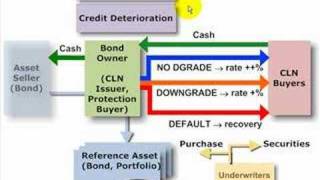
A CLN is similar to a credit default swap (CDS): both transfer credit risk to investors. However, the CLN is FUNDED; the bond owner does not really incur counterparty risk. Instead, the investors (CLN Buyers) incur counterparty risk. Plus, they are concerned with correlation between the CL
From playlist Derivatives: Credit Derivatives

Resilience brilliance: What did financial institutions learn in the past year?
Trevor Adams, Chief Risk Officer at Nedbank Group, rejoins RiskMinds International to reflect on banks' resilience in 2022, while giving us an update on the challenges around managing financial risks, particularly in South Africa. Find out more about RiskMinds International: https://bit.l
From playlist RiskMinds International 2022

Elimination of systamic risk in financial markets by Stefan Thurner
Program Summer Research Program on Dynamics of Complex Systems ORGANIZERS: Amit Apte, Soumitro Banerjee, Pranay Goel, Partha Guha, Neelima Gupte, Govindan Rangarajan and Somdatta Sinha DATE : 15 May 2019 to 12 July 2019 VENUE : Madhava hall for Summer School & Ramanujan hall f
From playlist Summer Research Program On Dynamics Of Complex Systems 2019

FRM: Basel internal ratings-based (IRB) risk weight function
Basel's IRB determines a capital charge (K) = Credit Value at Risk (CVaR) @ 99.9% – Expected Loss (UL). This function is estimating an unexpected loss (UL). For more financial risk videos, visit our website! http://www.bionicturtle.com
From playlist Basel

Low Default Portfolios (Part 1)
A Low Default Portfolio (LDP) is a portfolio characterized by a low number of defaults. Too simple? Citing the BCBS (Basel Committee on Banking Supervision): Several types of portfolios may have low numbers of defaults. For example, some portfolios historically have experienced low numb
From playlist Topics in Credit Risk Modelling