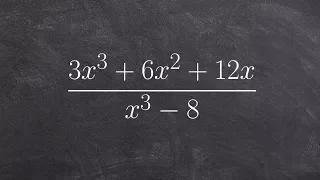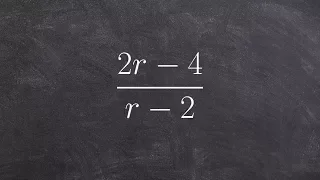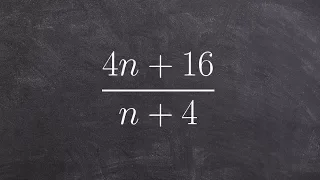Fractions (mathematics) | Number theory | Ring theory | Rational numbers
Dyadic rational
In mathematics, a dyadic rational or binary rational is a number that can be expressed as a fraction whose denominator is a power of two. For example, 1/2, 3/2, and 3/8 are dyadic rationals, but 1/3 is not. These numbers are important in computer science because they are the only ones with finite binary representations. Dyadic rationals also have applications in weights and measures, musical time signatures, and early mathematics education. They can accurately approximate any real number. The sum, difference, or product of any two dyadic rational numbers is another dyadic rational number, given by a simple formula. However, division of one dyadic rational number by another does not always produce a dyadic rational result. Mathematically, this means that the dyadic rational numbers form a ring, lying between the ring of integers and the field of rational numbers. This ring may be denoted . In advanced mathematics, the dyadic rational numbers are central to the constructions of the dyadic solenoid, Minkowski's question-mark function, Daubechies wavelets, Thompson's group, Prüfer 2-group, surreal numbers, and fusible numbers. These numbers are order-isomorphic to the rational numbers; they form a subsystem of the 2-adic numbers as well as of the reals, and can represent the fractional parts of 2-adic numbers. Functions from natural numbers to dyadic rationals have been used to formalize mathematical analysis in reverse mathematics. (Wikipedia).