
Trigonometry 5 The Cosine Relationship
A geometrical explanation of the law of cosines.
From playlist Trigonometry

From playlist Trigonometry TikToks

In this video on topics in emergency surgery for medical students and doctors, I discuss the common condition of biliary colic. Watch this video if your are preparing for the exams or are seeing a patient with biliary colic. Biliary colic is the most common form of gallstone disease, an
From playlist Let's talk Surgery

Lagrange Bicentenary - Cédric Villani's conference
From the stability of the Solar system to the stability of plasmas
From playlist Bicentenaire Joseph-Louis Lagrange
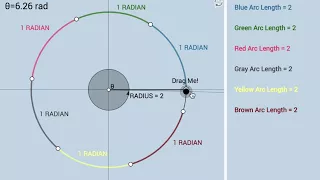
Radian Definition: Dynamic & Conceptual Illustrator
Link: https://www.geogebra.org/m/VYq5gSqU
From playlist Trigonometry: Dynamic Interactives!




