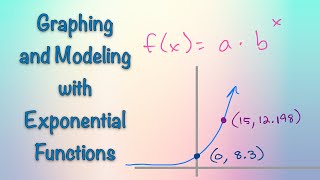
Applying Exponential Models // Math Minute [#34] [ALGEBRA]
Exponential functions work a lot like linear functions. There are typically two parameters that guide the use of the exponential function: the initial value (like the y-intercept of a linear function) and the factor of growth (like the slope of a linear function). There are some additional
From playlist Math Minutes

Determine if Equations Are Linear or Exponential and Increasing or Decreasing
This video explains how to identify linear and exponential equation as well as determine if the behavior is increasing or decreasing. http://mathispower4u.com
From playlist Introduction to Exponential Functions

Kurt Gödel Centenary - Part III
John W. Dawson, Jr. Pennsylvania State University November 17, 2006 More videos on http://video.ias.edu
From playlist Kurt Gödel Centenary

Seminar on Applied Geometry and Algebra (SIAM SAGA): Dustin Mixon
Title: Packing Points in Projective Spaces Speaker: Dustin Mixon Date: Tuesday, March 8, 2022 at 11:00am Eastern Abstract: Given a compact metric space, it is natural to ask how to arrange a given number of points so that the minimum distance is maximized. For example, the setting of the
From playlist Seminar on Applied Geometry and Algebra (SIAM SAGA)

Ex 2: Determine if a Table of Value Represents a Linear or Exponential Function (Fractions/Decimals)
This video explains how to determine if a table of values represents a linear function or an exponential function. http://mathispower4u.com
From playlist Introduction to Exponential Functions

Robert Ghrist (8/29/21): Laplacians and Network Sheaves
This talk will begin with a simple introduction to cellular sheaves as a generalized notion of a network of algebraic objects. With a little bit of geometry, one can often define a Laplacian for such sheaves. The resulting Hodge theory relates the geometry of the Laplacian to the algebraic
From playlist Beyond TDA - Persistent functions and its applications in data sciences, 2021

Introduction to Exponential Functions in the Form f(x)=ab^x - Part 1
This video introduces exponential growth and exponential decay functions in the form y=ab^x. http://mathispower4u.com
From playlist Introduction to Exponential Functions
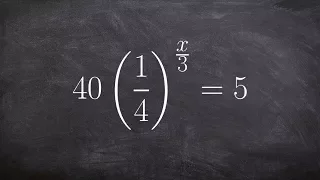
Solve an exponential equation using one to one property and isolating the exponent
👉 Learn how to solve exponential equations. An exponential equation is an equation in which a variable occurs as an exponent. To solve an exponential equation, we isolate the exponential part of the equation. Then we take the log of both sides. Note that the base of the log should correspo
From playlist Solve Exponential Equations with Logarithms

Interacting particle systems with kinetic constraints:.. (lecture 2) by Fabio Martinelli
PROGRAM: ADVANCES IN APPLIED PROBABILITY ORGANIZERS: Vivek Borkar, Sandeep Juneja, Kavita Ramanan, Devavrat Shah, and Piyush Srivastava DATE & TIME: 05 August 2019 to 17 August 2019 VENUE: Ramanujan Lecture Hall, ICTS Bangalore Applied probability has seen a revolutionary growth in resear
From playlist Advances in Applied Probability 2019
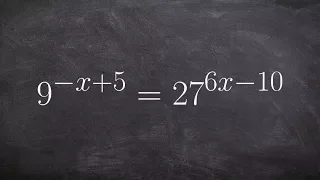
Using the equality of exponents to get the same base and solve
👉 Learn how to solve exponential equations. An exponential equation is an equation in which a variable occurs as an exponent. To solve an exponential equation, we isolate the exponential part of the equation. Then we take the log of both sides. Note that the base of the log should correspo
From playlist Solve Exponential Equations without a Calculator

Measurable equidecompositions – András Máthé – ICM2018
Analysis and Operator Algebras Invited Lecture 8.8 Measurable equidecompositions András Máthé Abstract: The famous Banach–Tarski paradox and Hilbert’s third problem are part of story of paradoxical equidecompositions and invariant finitely additive measures. We review some of the classic
From playlist Analysis & Operator Algebras
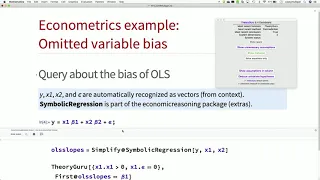
Automated Economic Reasoning with Mathematica
Casey Mulligan
From playlist Wolfram Technology Conference 2019
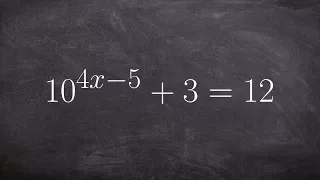
Use inverse operation to solve exponential equation without one to one property
👉 Learn how to solve exponential equations. An exponential equation is an equation in which a variable occurs as an exponent. To solve an exponential equation, we isolate the exponential part of the equation. Then we take the log of both sides. Note that the base of the log should correspo
From playlist Solve Exponential Equations with Logarithms

James Freitag, University of Illinois at Chicago
March 29, James Freitag, University of Illinois at Chicago Not Pfaffian
From playlist Spring 2022 Online Kolchin seminar in Differential Algebra

John Searle Interview on Perception & Philosophy of Mind
One of America’s most prominent philosophers says his field has been tilting at windmills for nearly 400 years. Representationalism (or indirect realism)---the idea that we don’t directly perceive external objects in the world, but only our own inner mental images or representations of obj
From playlist Philosophy of Mind

Learn basics for solving an exponential equation by using one to one property
👉 Learn how to solve exponential equations. An exponential equation is an equation in which a variable occurs as an exponent. To solve an exponential equation, we isolate the exponential part of the equation. Then we take the log of both sides. Note that the base of the log should correspo
From playlist Solve Exponential Equations with Logarithms

This Math Theorem Proves that 1=1+1 | The Banach-Tarskis Paradox
Mathematicians are in nearly universal agreement that the strangest paradox in math is the Banach-Tarski paradox, in which you can split one ball into a finite number of pieces, then rearrange the pieces to get two balls of the same size. Interestingly, only a minority of mathematicians ha
From playlist Math and Statistics
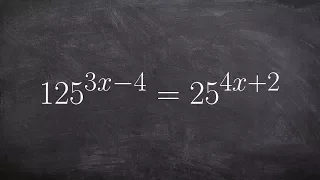
How to use the same base to solve an equation with exponents
👉 Learn how to solve exponential equations. An exponential equation is an equation in which a variable occurs as an exponent. To solve an exponential equation, we isolate the exponential part of the equation. Then we take the log of both sides. Note that the base of the log should correspo
From playlist Solve Exponential Equations without a Calculator
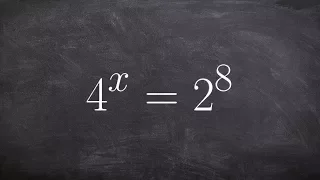
Learning to use the one to one property to solve an exponential equation
👉 Learn how to solve exponential equations. An exponential equation is an equation in which a variable occurs as an exponent. To solve an exponential equation, we isolate the exponential part of the equation. Then we take the log of both sides. Note that the base of the log should correspo
From playlist Solve Exponential Equations without a Calculator

Support Vsauce, your brain, Alzheimer's research, and other YouTube educators by joining THE CURIOSITY BOX: a seasonal delivery of viral science toys made by Vsauce! A portion of all proceeds goes to Alzheimer's research and our Inquisitive Fellowship, a program that gives money and resour
From playlist Science