Euclidean geometry | Linear algebra
Orthant
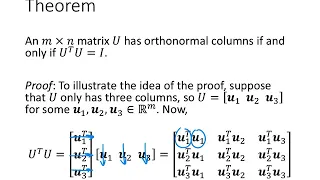
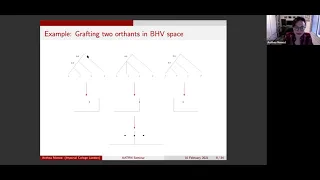
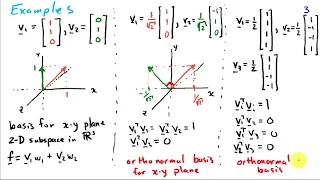
In geometry, an orthant or hyperoctant is the analogue in n-dimensional Euclidean space of a quadrant in the plane or an octant in three dimensions. In general an orthant in n-dimensions can be considered the intersection of n mutually orthogonal half-spaces. By independent selections of half-space signs, there are 2n orthants in n-dimensional space. More specifically, a closed orthant in Rn is a subset defined by constraining each Cartesian coordinate to be nonnegative or nonpositive. Such a subset is defined by a system of inequalities: ε1x1 ≥ 0 ε2x2 ≥ 0 · · · εnxn ≥ 0, where each εi is +1 or −1. Similarly, an open orthant in Rn is a subset defined by a system of strict inequalities ε1x1 > 0 ε2x2 > 0 · · · εnxn > 0, where each εi is +1 or −1. By dimension: * In one dimension, an orthant is a ray. * In two dimensions, an orthant is a quadrant. * In three dimensions, an orthant is an octant. John Conway defined the term n-orthoplex from orthant complex as a regular polytope in n-dimensions with 2n simplex facets, one per orthant. The nonnegative orthant is the generalization of the first quadrant to n-dimensions and is important in many constrained optimization problems. (Wikipedia).