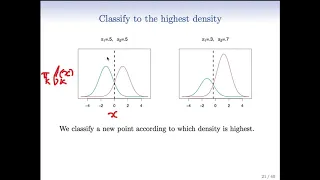
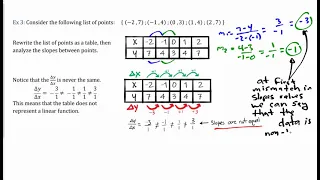
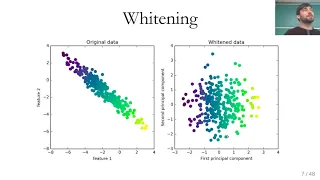
Classification algorithms | Statistical classification
Linear discriminant analysis
Linear discriminant analysis (LDA), normal discriminant analysis (NDA), or discriminant function analysis is a generalization of Fisher's linear discriminant, a method used in statistics and other fields, to find a linear combination of features that characterizes or separates two or more classes of objects or events. The resulting combination may be used as a linear classifier, or, more commonly, for dimensionality reduction before later classification. LDA is closely related to analysis of variance (ANOVA) and regression analysis, which also attempt to express one dependent variable as a linear combination of other features or measurements. However, ANOVA uses categorical independent variables and a continuous dependent variable, whereas discriminant analysis has continuous independent variables and a categorical dependent variable (i.e. the class label). Logistic regression and probit regression are more similar to LDA than ANOVA is, as they also explain a categorical variable by the values of continuous independent variables. These other methods are preferable in applications where it is not reasonable to assume that the independent variables are normally distributed, which is a fundamental assumption of the LDA method. LDA is also closely related to principal component analysis (PCA) and factor analysis in that they both look for linear combinations of variables which best explain the data. LDA explicitly attempts to model the difference between the classes of data. PCA, in contrast, does not take into account any difference in class, and factor analysis builds the feature combinations based on differences rather than similarities. Discriminant analysis is also different from factor analysis in that it is not an interdependence technique: a distinction between independent variables and dependent variables (also called criterion variables) must be made. LDA works when the measurements made on independent variables for each observation are continuous quantities. When dealing with categorical independent variables, the equivalent technique is discriminant correspondence analysis. Discriminant analysis is used when groups are known a priori (unlike in cluster analysis). Each case must have a score on one or more quantitative predictor measures, and a score on a group measure. In simple terms, discriminant function analysis is classification - the act of distributing things into groups, classes or categories of the same type. (Wikipedia).