
This video explains how to determine a unit vector given a vector. It also explains how to determine the component form of a vector in standard position that intersects the unit circle. http://mathispower4u.yolasite.com/
From playlist Vectors

What is the formula for component form of a vector
http://www.freemathvideos.com in this video series I will show you how to find the angle of a vector when given in component form or as a linear combination. To understand the direction of a vector it is important to go back to the unit circle and determine how we can find the angle when
From playlist Vectors
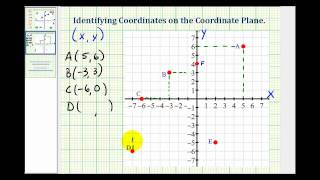
Ex: Identifying the Coordinates of Points on the Coordinate Plane
This video explains how to determine the coordinates of points on the coordinate plane. Complete Video List at http://www.mathispower4u.com Search by Topic at http://www.mathispower4u.wordpress.com
From playlist The Coordinate Plane, Plotting Points, and Solutions to Linear Equations in Two Variables

Ex: Find a Unit Vector in the Direction of a Given Vector in 3D
This example explains how to find a unit vector in the direction of a given vector in space. Site: http://mathispower4u.com
From playlist Vectors in Space (3D)

Ex: Find the Magnitude of a Vector in 3D
This video explains how to determine the magnitude of a vector in 3D. Site: http://mathispower4u.com
From playlist Vectors in Space (3D)
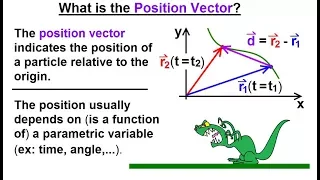
Calculus 3: Vector Calculus in 2D (17 of 39) What is the Position Vector?
Visit http://ilectureonline.com for more math and science lectures! In this video I will explain what is the position vector. The position vector indicates the position of a particle relative to the origin. The position usually depends on, or is a function of, a parametric variable (ex. t
From playlist CALCULUS 3 CH 3 VECTOR CALCULUS

What is the formula for a unit vector from a vector in component form
http://www.freemathvideos.com In this video series I will show you how to find the unit vector when given a vector in component form and as a linear combination. A unit vector is simply a vector with the same direction but with a magnitude of 1 and an initial point at the origin. It is i
From playlist Vectors
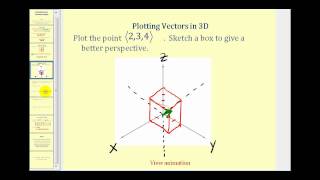
This video explains how to sketch vectors in R^3, how to determine the magnitude of a vector and how to determine a unit vector. http://mathispower4u.yolasite.com/
From playlist Vectors

What is a linear combination of your unit vectors
http://www.freemathvideos.com In this video series I will show you how to find the unit vector when given a vector in component form and as a linear combination. A unit vector is simply a vector with the same direction but with a magnitude of 1 and an initial point at the origin. It is i
From playlist Vectors - Understanding
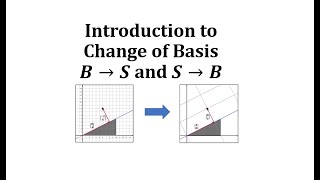
Introduction to Change of Basis
This video introduces a change of basis and show how to convert between the standard basis and a nonstandard basis coordinates.
From playlist Vectors: Change of Basis
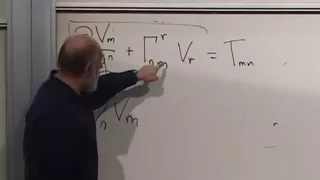
Einstein's General Theory of Relativity | Lecture 5
Lecture 5 of Leonard Susskind's Modern Physics concentrating on General Relativity. Recorded October 20, 2008 at Stanford University. This Stanford Continuing Studies course is the fourth of a six-quarter sequence of classes exploring the essential theoretical foundations of modern phys
From playlist Lecture Collection | Modern Physics: Einstein's Theory

What is General Relativity? Lesson 43: Holonomic and Non-Holonomic Basis
What is General Relativity? Lesson 43: Holonomic and Non-Holonomic Basis Since we have already discussed coordinate systems, basis vectors, and commutator, now is as good a time as any to talk about how 4 arbitrary vector fields may or may not be tangent vectors to coordinate curves. That
From playlist What is General Relativity?
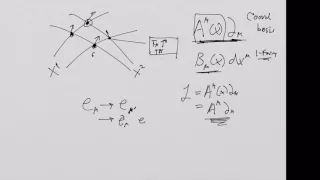
What is a Tensor 15: Coordinate Transformations
What is a Tensor 15: Coordinate Transformations
From playlist What is a Tensor?

WildLinAlg12: Generalized dilations and eigenvectors
This video introduces the important idea of changing coordinates in Linear Algebra. A linear transformation can be described using many different matrices, depending on the underlying coordinate system, or ordered basis, which is used to describe the space. The simplest case is when the
From playlist A first course in Linear Algebra - N J Wildberger
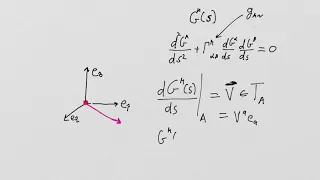
What is General Relativity? Lesson 54 - Scalar Curvature Part 3: Riemann Normal Coordinates
What is General Relativity? Lesson 54 -Scalar Curvature Part 3 Riemann Normal Coordinates This is the second of a few lectures about the Scalar Curvature and its interpretation. The goal is to get us to a point where we can have an interpretation of the Einstein Tensor and therefore an i
From playlist What is General Relativity?

Tensor Calculus 3a: The Covariant Basis
This course will eventually continue on Patreon at http://bit.ly/PavelPatreon Textbook: http://bit.ly/ITCYTNew Errata: http://bit.ly/ITAErrata McConnell's classic: http://bit.ly/MCTensors Table of Contents of http://bit.ly/ITCYTNew Rules of the Game Coordinate Systems and the Role of Te
From playlist Introduction to Tensor Calculus
Change of basis | Chapter 13, Essence of linear algebra
How do you translate back and forth between coordinate systems that use different basis vectors? Help fund future projects: https://www.patreon.com/3blue1brown An equally valuable form of support is to simply share some of the videos. Home page: https://www.3blue1brown.com/ Future series
From playlist Essence of linear algebra

What is General Relativity? Lesson 53: Scalar Curvature Part 2 - The Tetrad Formalism
What is General Relativity? Lesson 53: Scalar Curvature Part 2 - The Tetrad Formalism In this lecture we introduce the tetrad formalism. This is a pre-requisite, in my opinion, to the study of Riemann Normal Coordinates, although RNC are not always introduced with the tetrad formalism in
From playlist What is General Relativity?
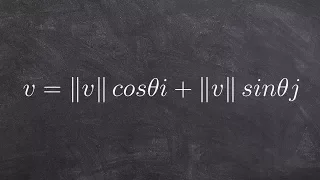
How do you understand the direction of an angle
Learn how to determine the magnitude and direction of a vector. The magnitude of a vector is the length of the vector. The magnitude of a vector is obtained by taking the square root of the sum of the squares of the components of the vector. The direction of a vector is obtained by taking
From playlist Vectors
