Matroid theory | Graph invariants | Computational problems | Polynomials | Duality theories
Tutte polynomial
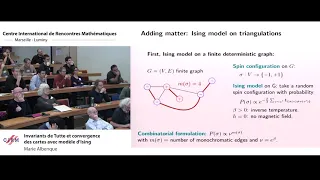
The Tutte polynomial, also called the dichromate or the Tutte–Whitney polynomial, is a graph polynomial. It is a polynomial in two variables which plays an important role in graph theory. It is defined for every undirected graph and contains information about how the graph is connected. It is denoted by . The importance of this polynomial stems from the information it contains about . Though originally studied in algebraic graph theory as a generalization of counting problems related to graph coloring and nowhere-zero flow, it contains several famous other specializations from other sciences such as the Jones polynomial from knot theory and the partition functions of the Potts model from statistical physics. It is also the source of several central computational problems in theoretical computer science. The Tutte polynomial has several equivalent definitions. It is equivalent to Whitney’s rank polynomial, Tutte’s own dichromatic polynomial and Fortuin–Kasteleyn’s random cluster model under simple transformations. It is essentially a generating function for the number of edge sets of a given size and connected components, with immediate generalizations to matroids. It is also the most general graph invariant that can be defined by a deletion–contraction recurrence. Several textbooks about graph theory and matroid theory devote entire chapters to it. (Wikipedia).