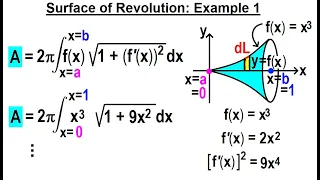
Surface of revolution
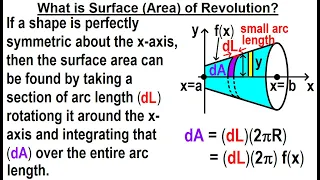
A surface of revolution is a surface in Euclidean space created by rotating a curve (the generatrix) around an axis of rotation. Examples of surfaces of revolution generated by a straight line are cylindrical and conical surfaces depending on whether or not the line is parallel to the axis. A circle that is rotated around any diameter generates a sphere of which it is then a great circle, and if the circle is rotated around an axis that does not intersect the interior of a circle, then it generates a torus which does not intersect itself (a ring torus). (Wikipedia).