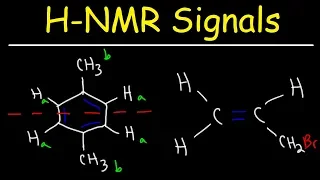
Signal
In signal processing, a signal is a function that conveys information about a phenomenon. Any quantity that can vary over space or time can be used as a signal to share messages between observers. The IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing includes audio, video, speech, image, sonar, and radar as examples of signal. A signal may also be defined as any observable change in a quantity over space or time (a time series), even if it does not carry information. In nature, signals can be actions done by an organism to alert other organisms, ranging from the release of plant chemicals to warn nearby plants of a predator, to sounds or motions made by animals to alert other animals of food. Signaling occurs in all organisms even at cellular levels, with cell signaling. Signaling theory, in evolutionary biology, proposes that a substantial driver for evolution is the ability of animals to communicate with each other by developing ways of signaling. In human engineering, signals are typically provided by a sensor, and often the original form of a signal is converted to another form of energy using a transducer. For example, a microphone converts an acoustic signal to a voltage waveform, and a speaker does the reverse. Another important property of a signal is its entropy or information content. Information theory serves as the formal study of signals and their content. The information of a signal is often accompanied by noise, which primarily refers to unwanted modifications of signals, but is often extended to include unwanted signals conflicting with desired signals (crosstalk). The reduction of noise is covered in part under the heading of signal integrity. The separation of desired signals from background noise is the field of signal recovery, one branch of which is estimation theory, a probabilistic approach to suppressing random disturbances. Engineering disciplines such as electrical engineering have advanced the design, study, and implementation of systems involving transmission, storage, and manipulation of information. In the latter half of the 20th century, electrical engineering itself separated into several disciplines: electronic engineering and computer engineering developed to specialize in the design and analysis of systems that manipulate physical signals, while design engineering developed to address the functional design of signals in user–machine interfaces. (Wikipedia).