
integration by partial fractions with an irreducible quadratic factor
Learn how to do this integral of a rational function by using partial fraction decomposition. This integration has a cubic denominator and we will see how to factor it to get a linear factor and an irreducible quadratic factor. For more calculus tutorials, check out my new channel @just
From playlist Integration by Partial Fractions, Calculus 2

Summary for simplifying complex fractions
👉 Learn how to simplify a complex fraction. A complex fraction is a fraction with another fraction or fractions in the numerator and/or in the denominator. To simplify a complex fraction is to reduce the fraction in such a way as there is only one numerator and denominator. In doing that,
From playlist How to Simplify Complex Fractions | Learn About

Overview of Complex Fractions and Solving Rational Equations
👉 Learn how to simplify a complex fraction. A complex fraction is a fraction with another fraction or fractions in the numerator and/or in the denominator. To simplify a complex fraction is to reduce the fraction in such a way as there is only one numerator and denominator. In doing that,
From playlist How to Simplify Complex Fractions | Learn About

How do you Simplify Complex Fractions
👉 Learn how to simplify a complex fraction. A complex fraction is a fraction with another fraction or fractions in the numerator and/or in the denominator. To simplify a complex fraction is to reduce the fraction in such a way as there is only one numerator and denominator. In doing that,
From playlist How to Simplify Complex Fractions | Learn About

How do you Simplify Complex Fractions
👉 Learn how to simplify a complex fraction. A complex fraction is a fraction with another fraction or fractions in the numerator and/or in the denominator. To simplify a complex fraction is to reduce the fraction in such a way as there is only one numerator and denominator. In doing that,
From playlist How to Simplify Complex Fractions | Learn About

👉 Learn how to simplify a complex fraction. A complex fraction is a fraction with another fraction or fractions in the numerator and/or in the denominator. To simplify a complex fraction is to reduce the fraction in such a way as there is only one numerator and denominator. In doing that,
From playlist How to Simplify Complex Fractions | Learn About

What do you need to know when simplifying complex fractions
👉 Learn how to simplify a complex fraction. A complex fraction is a fraction with another fraction or fractions in the numerator and/or in the denominator. To simplify a complex fraction is to reduce the fraction in such a way as there is only one numerator and denominator. In doing that,
From playlist How to Simplify Complex Fractions | Learn About
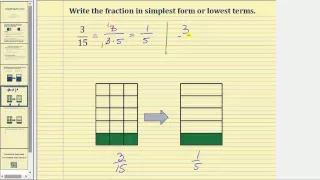
This video defines what a simplified fraction is and explains how to simplify fractions using prime factors and division.
From playlist Simplifying Fractions

Overview of fractions - free math help - online tutor
👉 Learn how to understand the concept of fractions using parts of a whole. Fractions are parts of a whole and this concept can be illustrated using bars and circles. This concept can also be extended to understand equivalent fractions. When a whole bar is divided into, say, two equal parts
From playlist Learn About Fractions
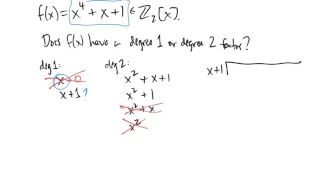
In this video I discuss irreducible polynomials and tests for irreducibility. Note that this video is intended for students in abstract algebra and is not appropriate for high-school or early college level algebra courses.
From playlist Abstract Algebra

Partial Fractions #2 (OpenStax Calculus, Vol. 2, Section 3.4)
This video contains solutions to sample problems from OpenStax Calculus, Volume 2, Section 3.4: Partial Fractions. This is the second of two videos, focusing on more complicated examples involving repeated factors and/or irreducible quadratic factors. OpenStax Calculus Vol. 2: https://op
From playlist Calculus II

Partial Fractions | Repeating and irreducible Quadratic Terms
While in the Intro to Partial Fractions video we largely focused on decomposing rational functions whose denominators were products of non-repeating linear terms, in this video we investigate what happens if the factors are either repeating or irreducible quadratics (i.e. they can not be f
From playlist Calculus II (Integration Methods, Series, Parametric/Polar, Vectors) **Full Course**
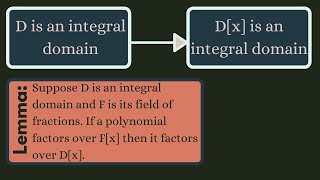
Abstract Algebra | If D is a UFD then D[x] is a UFD.
We prove an important result that states the ring of polynomials whose coefficients are from a unique factorization domain is itself a unique factorization domain. Along the way, we define the content of a polynomial, prove Gauss' lemma, and prove that if a polynomial factors over the fiel
From playlist Abstract Algebra

How to integrate ANY rational function (ratio/quotient/division of two polynomials)
In this video we consider the problem of how to integrate any rational function - that is a quotient/ratio/division of any two other polynomials. This video gives a map of how to go about every different case, requiring the use of many techniques of A-level maths and further mathematics.
From playlist FP3 Calculus involving inverse hyperbolic and trigonemtric functions
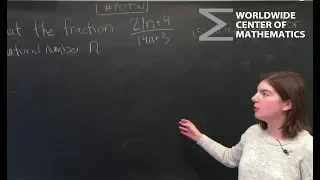
PotW: Prove that the Fraction is Irreducible [Number Theory]
If this video is confusing, be sure to check out our blog for the full solution transcript! https://centerofmathematics.blogspot.com/2018/10/problem-of-week-10-18-18-prove-that.html
From playlist Center of Math: Problems of the Week

Ring Theory: We consider general polynomial rings over an integral domain. In this part, we show that polynomial rings over integral domains are integral domains, and we prove Gauss' Lemma as a step in showing that polynomial rings over UFDs are UFDs.
From playlist Abstract Algebra

The First International Math Olympiad Problem [IMO 1959 Problem 1]
Today we solve the very first problem from the very first International Mathematical Olympiad competition, from way back in 1959! This problem asks us to prove the fraction (21n+4)/(14n+3) is irreducible for every natural number n. This first problem was suggested by Poland, and the compet
From playlist Coffee Time Math with Wrath of Math

Anthony Henderson: Hilbert Schemes Lecture 4
SMRI Seminar Series: 'Hilbert Schemes' Lecture 4 Kleinian singularities 1 Anthony Henderson (University of Sydney) This series of lectures aims to present parts of Nakajima’s book `Lectures on Hilbert schemes of points on surfaces’ in a way that is accessible to PhD students interested i
From playlist SMRI Course: Hilbert Schemes

Finding ALL Solutions of Polynomials (Precalculus - College Algebra 37)
Support: https://www.patreon.com/ProfessorLeonard Professor Leonard Merch: https://professor-leonard.myshopify.com How to completely factor a polynomial over the complex number system and find all of the solutions, including complex.
From playlist Precalculus - College Algebra/Trigonometry

Ex 1: Determine Equivalent Fractions to a Given Fraction
This video provides an example of how to determine several equivalent fractions to a given fraction. Search Complete Library: http://www.mathispower4u.wordpress.com
From playlist Introduction to Fractions