What are Non-Classical logics?
Some of the general classes of non-classical logics I touch in this videos are linear logic, relevant logic, modal logic, many-valued logics, minimal logic, paraconsistent logics and so on and so forth. Let me know if I should dive deeping into a certain scene? https://en.wikipedia.org/wi
From playlist Programming

Pre-Calculus - The vocabulary of linear functions and equations
This video will introduce you to a few of the terms that are commonly used with linear functions and equations. Pay close attention to how you can tell the difference between linear and non-linear functions. For more videos please visit http://www.mysecretmathtutor.com
From playlist Pre-Calculus

Logic: The Structure of Reason
As a tool for characterizing rational thought, logic cuts across many philosophical disciplines and lies at the core of mathematics and computer science. Drawing on Aristotle’s Organon, Russell’s Principia Mathematica, and other central works, this program tracks the evolution of logic, be
From playlist Logic & Philosophy of Mathematics

Propositional Logic and the Algebra of Boole | MathFoundations273 | N J Wildberger
We give an overview of classical Propositional Logic, which is a branch of philosophy concerned with systematizing reason. This framework uses "atomic statements" called "propositions", and "relations", or "connectives", between them, prominently AND, OR, NOT, IMPLIES and EQUIVALENT, and t
From playlist Boole's Logic and Circuit Analysis

Infinitesimals in Synthetic Differential Geometry
In this video I describe the logic of Synthetic Differential Geometry. This is a non-constructive theory collapsing in the presence of the law of excluded middle. As a logic al theory, it can be realized in a topos and it has sheave models giving a nice representation of tangent bundles.
From playlist Algebra

An introduction to the general types of logic statements
From playlist Geometry

A Defense of Classical Theology (Part 2): God is not a god
In part 2 of this series, we're going to make it quite clear that God as understood in the classical theistic tradition has nothing to do with 'the gods' of pagan polytheism and represents a totally different order of reality. This confusion is at epidemic levels in popular discourse, whic
From playlist Theology
How to Get Classical Physics from Quantum Mechanics
We tend to think of Classical Physics as straightforward and intuitive and Quantum Mechanics as difficult and conceptually challenging. However, this is not always the case! In classical mechanics, a standard technique for finding the evolution equations for a system is the method of least
From playlist Quantum Mechanics

Samson Abramsky - The sheaf-theoretic structure of contextuality and non-locality
Talk at the school and conference “Toposes online” (24-30 June 2021): https://aroundtoposes.com/toposesonline/ Slides: https://aroundtoposes.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/AbramskySlidesToposesOnline.pdf Quantum mechanics implies a fundamentally non-classical picture of the physical worl
From playlist Toposes online

Classical and Quantum Subjectivity
Uncertainty is a major component of subjective logic beliefs. We discuss the cloud of uncertainty across Markov networks, insights from computational irreducibility, and negative quantum quasiprobabilities and beliefs.
From playlist Wolfram Technology Conference 2022

Quantum Technology: Concepts and Prospects by Apoorva D. Patel
ICTS Colloquium Tittle : Quantum Technology - Concepts and Prospects Speaker : Apoorva D. Patel (Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore) DATE : Monday,November 25,2019 Time : 02:30PM VENUE : Madhava Lecture Hall, ICTS Campus Bangalore Abstract : A variety of
From playlist ICTS Colloquia

Micaela Mayero - Overview of real numbers in theorem provers: application with real analysis in Coq
Recorded 15 February 2023. Micaela Mayero of the Galilee Institute - Paris Nord University presents "An overview of the real numbers in theorem provers: an application with real analysis in Coq" at IPAM's Machine Assisted Proofs Workshop. Abstract: Formalizing real numbers in a formal proo
From playlist 2023 Machine Assisted Proofs Workshop

Fundamentals of Mathematics - Lecture 33: Dedekind's Definition of Infinite Sets are FInite Sets
https://www.uvm.edu/~tdupuy/logic/Math52-Fall2017.html
From playlist Fundamentals of Mathematics

What is quantum mechanics? A minimal formulation (Seminar) by Pierre Hohenberg
29 December 2017 VENUE : Ramanujan Lecture Hall, ICTS , Bangalore This talk asks why the interpretation of quantum mechanics, in contrast to classical mechanics is still a subject of controversy, and presents a 'minimal formulation' modeled on a formulation of classical mechanics. In bot
From playlist US-India Advanced Studies Institute: Classical and Quantum Information
Cohomological representations of real reductive groups by Arvind Nair
PROGRAM : ALGEBRAIC AND ANALYTIC ASPECTS OF AUTOMORPHIC FORMS ORGANIZERS : Anilatmaja Aryasomayajula, Venketasubramanian C G, Jurg Kramer, Dipendra Prasad, Anandavardhanan U. K. and Anna von Pippich DATE & TIME : 25 February 2019 to 07 March 2019 VENUE : Madhava Lecture Hall, ICTS Banga
From playlist Algebraic and Analytic Aspects of Automorphic Forms 2019

Paola Cantù : Logic and Interaction:pragmatics and argumentation theory
HYBRID EVENT Recorded during the meeting "Logic and transdisciplinarity" the February 11, 2022 by the Centre International de Rencontres Mathématiques (Marseille, France) Filmmaker: Guillaume Hennenfent Find this video and other talks given by worldwide mathematicians on CIRM's Audiov
From playlist Logic and Foundations

Olivia Caramello - 1/4 Introduction to Grothendieck toposes
This course provides an introduction to the theory of Grothendieck toposes from a meta-mathematical point of view. It presents the main classical approaches to the subject (namely, toposes as generalized spaces, toposes as mathematical universes and toposes as classifiers of models of firs
From playlist Olivia Caramello - Introduction to Grothendieck toposes
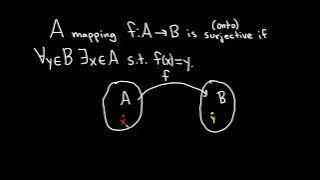
Definition of a Surjective Function and a Function that is NOT Surjective
We define what it means for a function to be surjective and explain the intuition behind the definition. We then do an example where we show a function is not surjective. Surjective functions are also called onto functions. Useful Math Supplies https://amzn.to/3Y5TGcv My Recording Gear ht
From playlist Injective, Surjective, and Bijective Functions