
What is an integral and it's parts
👉 Learn about integration. The integral, also called antiderivative, of a function, is the reverse process of differentiation. Integral of a function can be evaluated as an indefinite integral or as a definite integral. A definite integral is an integral in which the upper and the lower li
From playlist The Integral

Apply u substitution to a polynomial
👉 Learn how to evaluate the integral of a function. The integral, also called antiderivative, of a function, is the reverse process of differentiation. Integral of a function can be evaluated as an indefinite integral or as a definite integral. A definite integral is an integral in which t
From playlist The Integral

Learn how to use u substitution to integrate a polynomial
👉 Learn how to evaluate the integral of a function. The integral, also called antiderivative, of a function, is the reverse process of differentiation. Integral of a function can be evaluated as an indefinite integral or as a definite integral. A definite integral is an integral in which t
From playlist The Integral
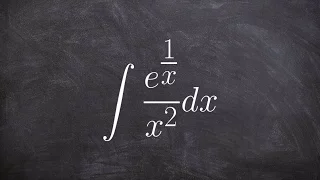
How to integrate exponential expression with u substitution
👉 Learn how to evaluate the integral of a function. The integral, also called antiderivative, of a function, is the reverse process of differentiation. Integral of a function can be evaluated as an indefinite integral or as a definite integral. A definite integral is an integral in which t
From playlist The Integral

Integrate cosine using u substitution
👉 Learn how to evaluate the integral of a function. The integral, also called antiderivative, of a function, is the reverse process of differentiation. Integral of a function can be evaluated as an indefinite integral or as a definite integral. A definite integral is an integral in which t
From playlist The Integral

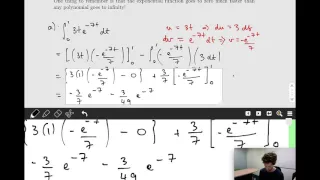
Dirichlet Eta Function - Integral Representation
Today, we use an integral to derive one of the integral representations for the Dirichlet eta function. This representation is very similar to the Riemann zeta function, which explains why their respective infinite series definition is quite similar (with the eta function being an alte rna
From playlist Integrals

How to use u substitution to find the indifinite integral
👉 Learn how to evaluate the integral of a function. The integral, also called antiderivative, of a function, is the reverse process of differentiation. Integral of a function can be evaluated as an indefinite integral or as a definite integral. A definite integral is an integral in which t
From playlist The Integral

Learn how to integrate a rational expression by simplifying first with rational powers
👉 Learn how to evaluate the integral of a function. The integral, also called antiderivative, of a function, is the reverse process of differentiation. Integral of a function can be evaluated as an indefinite integral or as a definite integral. A definite integral is an integral in which t
From playlist The Integral

Integral Transforms Lecture 7: The Fourier Transform. Oxford Mathematics 2nd Year Student Lecture
This short course from Sam Howison, all 9 lectures of which we are making available (this is lecture 7), introduces two vital ideas. First, we look at distributions (or generalised functions) and in particular the mathematical representation of a 'point mass' as the Dirac delta function.
From playlist Oxford Mathematics Student Lectures - Integral Transforms

Compositional Structure of Classical Integral Transforms
The recently implemented fractional order integro-differentiation operator, FractionalD, is a particular case of more general integral transforms. The majority of classical integral transforms are representable as compositions of only two transforms: the modified direct and inverse Laplace
From playlist Wolfram Technology Conference 2022
MATH2018 Lecture 7.1 Laplace Transforms
We introduce the concept of a Laplace Transform, which allows us to change a function f(t) into a new function F(s) that is easier to deal with. This is really useful if there are discontinuities in our original function.
From playlist MATH2018 Engineering Mathematics 2D

ME565 Lecture 21: The Laplace Transform
ME565 Lecture 21 Engineering Mathematics at the University of Washington Laplace Transform Notes: http://faculty.washington.edu/sbrunton/me565/pdf/L21.pdf Course Website: http://faculty.washington.edu/sbrunton/me565/ http://faculty.washington.edu/sbrunton/
From playlist Engineering Mathematics (UW ME564 and ME565)

Lecture 8 | The Fourier Transforms and its Applications
Lecture by Professor Brad Osgood for the Electrical Engineering course, The Fourier Transforms and its Applications (EE 261). Professor Osgood continues lecturing on the general properties of the Fourier Transforms by two paths. First, to develop specific transforms and second, to unders
From playlist Lecture Collection | The Fourier Transforms and Its Applications

Lecture 7 | The Fourier Transforms and its Applications
Lecture by Professor Brad Osgood for the Electrical Engineering course, The Fourier Transforms and its Applications (EE 261). Professor Osgood reintroduces the Fourier Transform and its inverse, then he goes into specific properties and transforms. The Fourier transform is a tool for s
From playlist Lecture Collection | The Fourier Transforms and Its Applications

Integral Transforms - Lecture 8: The Fourier Inversion Theorem. Oxford Maths 2nd Yr Student Lecture
This short course from Sam Howison, all 9 lectures of which we are making available (this is lecture 8), introduces two vital ideas. First, we look at distributions (or generalised functions) and in particular the mathematical representation of a 'point mass' as the Dirac delta function.
From playlist Oxford Mathematics Student Lectures - Integral Transforms

Lecture 6 | The Fourier Transforms and its Applications
Lecture by Professor Brad Osgood for the Electrical Engineering course, The Fourier Transforms and its Applications (EE 261). Professor Osgood picks up where he left off last lecture on Fourier Transformations, then he launches into a more formal treatment of Fourier transforms and explai
From playlist Fourier

Differential Equations: Laplace Transform of Polynomials
The Laplace transform of a polynomial, by linearity, may be broken down into scaled Laplace transforms of powers of t. Prevalent as polynomials are, it would therefore be useful to know what the Laplace transform of t to the power of n is. In this video, I explain such a formula by inducti
From playlist Differential Equations

Complex Analysis L13: Bromwich Integrals and the Inverse Laplace Transform
This video is a culmination of this series on complex analysis, where we show how to compute the Bromwich integral used in the inverse Laplace transform. @eigensteve on Twitter eigensteve.com databookuw.com
From playlist Engineering Math: Crash Course in Complex Analysis

Lecture 11 | The Fourier Transforms and its Applications
Lecture by Professor Brad Osgood for the Electrical Engineering course, The Fourier Transforms and its Applications (EE 261). Professor Osgood lectures on confronting the convergence of intervals. The Fourier transform is a tool for solving physical problems. In this course the emphasi
From playlist Lecture Collection | The Fourier Transforms and Its Applications
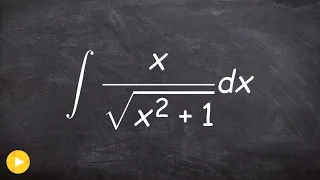
How to integrate when there is a radical in the denominator
👉 Learn how to evaluate the integral of a function. The integral, also called antiderivative, of a function, is the reverse process of differentiation. Integral of a function can be evaluated as an indefinite integral or as a definite integral. A definite integral is an integral in which t
From playlist The Integral