
Differential Equations: A Double Root of the Characteristic Equation
Homogeneous, constant-coefficient differential equations have a characteristic or auxiliary equation. The solution(s) of this equation yield the particular solutions to the homogeneous differential equation which, when combined, produce a general solution. In this video, we explore the tri
From playlist Differential Equations
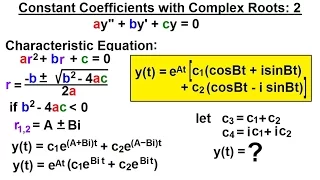
Differential Equation - 2nd Order (21 of 54) Constant Coeff. w/ Complex Roots: Another Look
Visit http://ilectureonline.com for more math and science lectures! In this video I will find y(t)=?, given ay”+by'+cy=0 assuming the characteristic equation roots are complex. Next video in this series can be seen at: https://youtu.be/QuR7-rVm8Q8
From playlist DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS 11 - 2nd ORDER, A COMPLETE OVERVIEW

Derivation of the Characteristic Equation | Linear Algebra -- Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors
In this video, we look at the intuition behind eigenvalues and eigenvectors. In particular, we offer a derivation of the characteristic equation and relate to this to the geometric meaning behind eigenvalues and eigenvectors. We derive the characteristic equation for calculating eigenvalue
From playlist Linear Algebra

(2.3.102) Given a Roots of a Characteristic Equation, Find the 3rd Order DE and General Solutions
This video explains how to determine the characteristic equation, differential equation, and general solution given the roots of the characteristic equation. https://mathispower4u.com
From playlist Differential Equations: Complete Set of Course Videos
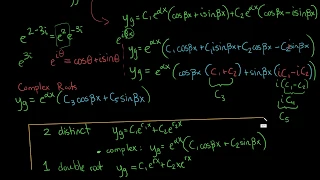
Differential Equations: Complex Roots of the Characteristic Equation
Homogeneous, constant-coefficient differential equations have a characteristic or auxiliary equation. The solution(s) of this equation yield the particular solutions to the homogeneous differential equation which, when combined, produce a general solution. In this video, we explore the cas
From playlist Differential Equations
Linear Algebra - Lecture 34 - The Characteristic Equation
In this lecture, we discuss the characteristic equation of a square matrix. This equation is used to compute the eigenvalues for that matrix.
From playlist Linear Algebra Lectures

How to solve a differentialble equation by separating the variables
Learn how to solve the particular solution of differential equations. A differential equation is an equation that relates a function with its derivatives. The solution to a differential equation involves two parts: the general solution and the particular solution. The general solution give
From playlist Solve Differential Equation (Particular Solution) #Integration

(2.3.4) Given a Characteristic Equation, Find the 3rd Order DE and General Solutions
This video explains how to determine the characteristic equation, differential equation, and general solution given the factored form of the characteristic equation. https://mathispower4u.com
From playlist Differential Equations: Complete Set of Course Videos

Method of Characteristics: How to solve PDE
Free ebook https://bookboon.com/en/partial-differential-equations-ebook How to solve PDE via the method of characteristics. An example involving a semi linear PDE is presented, plus we discuss why the ideas work. Such a technique is used in solving a wide range of problems.
From playlist Partial differential equations

How to Solve the Linear Third Order Differential Equation y''' - 6y'' + 11y' - 6y = 0
How to Solve the Linear Third Order Differential Equation y''' - 6y'' + 11y' - 6y = 0 If you enjoyed this video please consider liking, sharing, and subscribing. Udemy Courses Via My Website: https://mathsorcerer.com My FaceBook Page: https://www.facebook.com/themathsorcerer There ar
From playlist Homogeneous Linear Differential Equations with Constant Coefficients
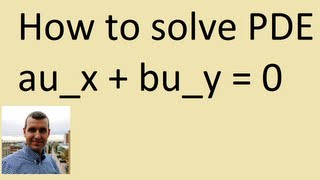
How to solve PDE via method of characteristics
Free ebook https://bookboon.com/en/partial-differential-equations-ebook Basic example showing how to solve PDE via method of characteristics. A general first order problem is solved with a concrete example discussed at the end. The ideas can be used to solve many kinds of first order par
From playlist Differential equations

Second order differential equation: real and unequal roots
Free ebook http://bookboon.com/en/learn-calculus-2-on-your-mobile-device-ebook How to solve second order differential equations. An example with real and unequal roots to the characteristic equation is discussed.
From playlist Differential equations

Solve the Differential Equation y'' - 9y = 54 using the Annihilator Method
Solve the Differential Equation y'' - 9y = 54 using the Annihilator Method If you enjoyed this video please consider liking, sharing, and subscribing. Udemy Courses Via My Website: https://mathsorcerer.com My FaceBook Page: https://www.facebook.com/themathsorcerer There are several way
From playlist Differential Operators and the Annihilator Method

Higher Order Constant Coefficient Differential Equations: y'''+y'=0 and y''''-3y'''+3y''-y'=0
MY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS PLAYLIST: ►https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLHXZ9OQGMqxde-SlgmWlCmNHroIWtujBw Open Source (i.e free) ODE Textbook: ►http://web.uvic.ca/~tbazett/diffyqs In the previous videos in our ODE playlist we have seen how to solve constant coefficient homogeneous sec
From playlist Ordinary Differential Equations (ODEs)

Solve y'' - 4y = 0 If you enjoyed this video please consider liking, sharing, and subscribing. Udemy Courses Via My Website: https://mathsorcerer.com My FaceBook Page: https://www.facebook.com/themathsorcerer There are several ways that you can help support my channel:) Consider becom
From playlist Homogeneous Linear Differential Equations with Constant Coefficients

PDE and method of characteristics: a how to
Free ebook https://bookboon.com/en/partial-differential-equations-ebook Example illustrating the method of characteristics. Such ideas are used to solve partial differential equations (PDEs).
From playlist Partial differential equations

The definition of the characteristic polynomial (without using determinants). The Cayley-Hamilton Theorem.
From playlist Linear Algebra Done Right

Ch3Pr30: Homogenous Second Degree Differential Equation
How to solve a differential equations of the second degree y'' + 3y' + 2y = 0. This is Chapter 3 Problem 30 from the MATH1231/1241 Calculus notes. Presented by Galina Levitina from the UNSW School of Mathematics and Statisitcs.
From playlist Mathematics 1B (Calculus)

