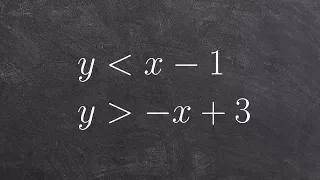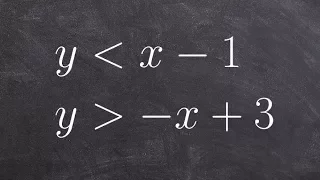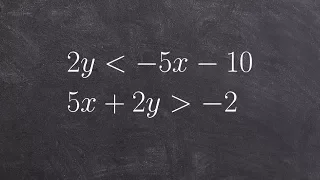Geometric graphs | Perfect graphs | Intersection classes of graphs
Indifference graph
In graph theory, a branch of mathematics, an indifference graph is an undirected graph constructed by assigning a real number to each vertex and connecting two vertices by an edge when their numbers are within one unit of each other. Indifference graphs are also the intersection graphs of sets of unit intervals, or of properly nested intervals (intervals none of which contains any other one). Based on these two types of interval representations, these graphs are also called unit interval graphs or proper interval graphs; they form a subclass of the interval graphs. (Wikipedia).