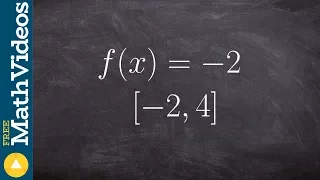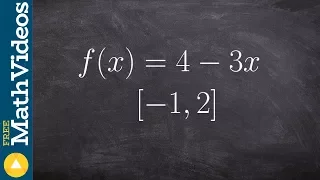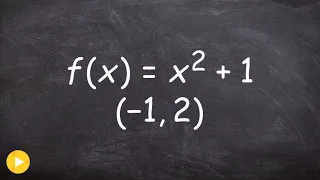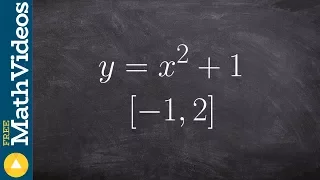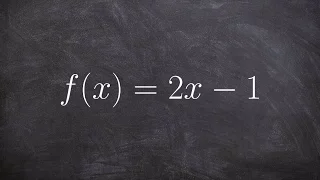Articles containing proofs | Theorems in real analysis | Theorems in calculus
Extreme value theorem
In calculus, the extreme value theorem states that if a real-valued function is continuous on the closed interval , then must attain a maximum and a minimum, each at least once. That is, there exist numbers and in such that: The extreme value theorem is more specific than the related boundedness theorem, which states merely that a continuous function on the closed interval is bounded on that interval; that is, there exist real numbers and such that: This does not say that and are necessarily the maximum and minimum values of on the interval which is what the extreme value theorem stipulates must also be the case. The extreme value theorem is used to prove Rolle's theorem. In a formulation due to Karl Weierstrass, this theorem states that a continuous function from a non-empty compact space to a subset of the real numbers attains a maximum and a minimum. (Wikipedia).