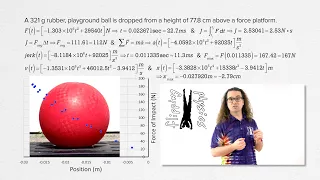
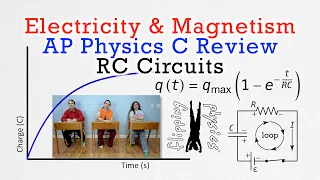
Time
Time is the continued sequence of existence and events that occurs in an apparently irreversible succession from the past, through the present, into the future. It is a component quantity of various measurements used to sequence events, to compare the duration of events or the intervals between them, and to quantify rates of change of quantities in material reality or in the conscious experience. Time is often referred to as a fourth dimension, along with three spatial dimensions. Time has long been an important subject of study in religion, philosophy, and science, but defining it in a manner applicable to all fields without circularity has consistently eluded scholars.Nevertheless, diverse fields such as business, industry, sports, the sciences, and the performing arts all incorporate some notion of time into their respective measuring systems. Time in physics is operationally defined as "what a clock reads". The physical nature of time is addressed by general relativity with respect to events in spacetime. Examples of events are the collision of two particles, the explosion of a supernova, or the arrival of a rocket ship. Every event can be assigned four numbers representing its time and position (the event's coordinates). However, the numerical values are different for different observers. In general relativity, the question of what time it is now only has meaning relative to a particular observer. Distance and time are intimately related, and the time required for light to travel a specific distance is the same for all observers, as first publicly demonstrated by Michelson and Morley. General relativity does not address the nature of time for extremely small intervals where quantum mechanics holds. At this time, there is no generally accepted theory of quantum general relativity. Time is one of the seven fundamental physical quantities in both the International System of Units (SI) and International System of Quantities. The SI base unit of time is the second, which is defined by measuring the electronic transition frequency of caesium atoms. Time is used to define other quantities, such as velocity, so defining time in terms of such quantities would result in circularity of definition. An operational definition of time, wherein one says that observing a certain number of repetitions of one or another standard cyclical event (such as the passage of a free-swinging pendulum) constitutes one standard unit such as the second, is highly useful in the conduct of both advanced experiments and everyday affairs of life. To describe observations of an event, a location (position in space) and time are typically noted. The operational definition of time does not address what the fundamental nature of it is. It does not address why events can happen forward and backward in space, whereas events only happen in the forward progress of time. Investigations into the relationship between space and time led physicists to define the spacetime continuum. General relativity is the primary framework for understanding how spacetime works. Through advances in both theoretical and experimental investigations of spacetime, it has been shown that time can be distorted and dilated, particularly at the edges of black holes. Temporal measurement has occupied scientists and technologists and was a prime motivation in navigation and astronomy. Periodic events and periodic motion have long served as standards for units of time. Examples include the apparent motion of the sun across the sky, the phases of the moon, and the swing of a pendulum. Time is also of significant social importance, having economic value ("time is money") as well as personal value, due to an awareness of the limited time in each day and in human life spans. There are many systems for determining what time it is, including the Global Positioning System, other satellite systems, Coordinated Universal Time and mean solar time. In general, the numbers obtained from different time systems differ from one another. (Wikipedia).