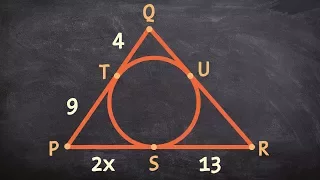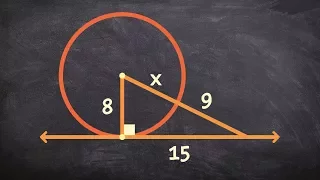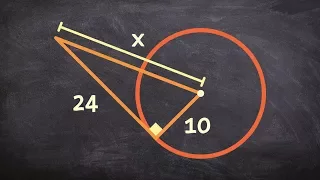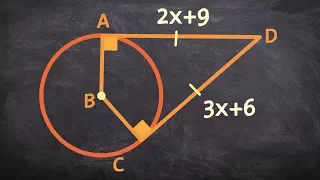Objects defined for a triangle
Tangential triangle
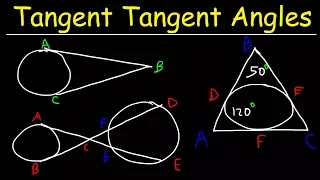
In geometry, the tangential triangle of a reference triangle (other than a right triangle) is the triangle whose sides are on the tangent lines to the reference triangle's circumcircle at the reference triangle's vertices. Thus the incircle of the tangential triangle coincides with the circumcircle of the reference triangle. The circumcenter of the tangential triangle is on the reference triangle's Euler line, as is the center of similitude of the tangential triangle and the orthic triangle (whose vertices are at the feet of the altitudes of the reference triangle). The tangential triangle is homothetic to the orthic triangle. A reference triangle and its tangential triangle are in perspective, and the axis of perspectivity is the Lemoine axis of the reference triangle. That is, the lines connecting the vertices of the tangential triangle and the corresponding vertices of the reference triangle are concurrent. The center of perspectivity, where these three lines meet, is the symmedian point of the triangle. The tangent lines containing the sides of the tangential triangle are called the exsymmedians of the reference triangle. Any two of these are concurrent with the third symmedian of the reference triangle. The reference triangle's circumcircle, its nine-point circle, its polar circle, and the circumcircle of the tangential triangle are coaxal. A right triangle has no tangential triangle, because the tangent lines to its circumcircle at its acute vertices are parallel and thus cannot form the sides of a triangle. The reference triangle is the Gergonne triangle of the tangential triangle. (Wikipedia).