Circles defined for a triangle
Polar circle (geometry)
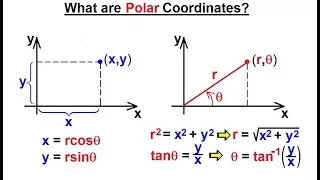
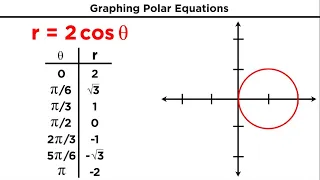
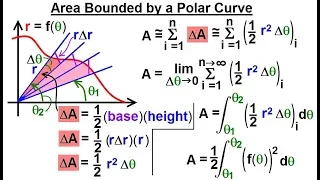
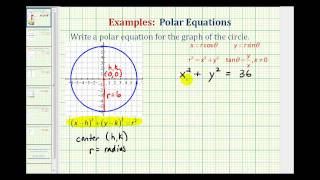
In geometry, the polar circle of a triangle is the circle whose center is the triangle's orthocenter and whose squared radius is where A, B, C denote both the triangle's vertices and the angle measures at those vertices, H is the orthocenter (the intersection of the triangle's altitudes), D, E, F are the feet of the altitudes from vertices A, B, C respectively, R is the triangle's circumradius (the radius of its circumscribed circle), and a, b, c are the lengths of the triangle's sides opposite vertices A, B, C respectively. The first parts of the radius formula reflect the fact that the orthocenter divides the altitudes into segment pairs of equal products. The trigonometric formula for the radius shows that the polar circle has a real existence only if the triangle is obtuse, so one of its angles is obtuse and hence has a negative cosine. (Wikipedia).