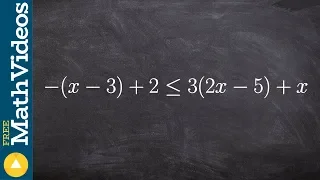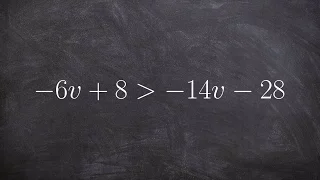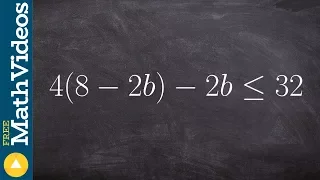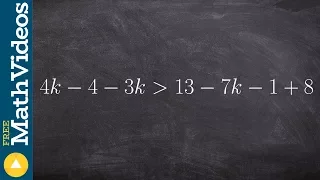Ptolemy's inequality
In Euclidean geometry, Ptolemy's inequality relates the six distances determined by four points in the plane or in a higher-dimensional space. It states that, for any four points A, B, C, and D, the following inequality holds: It is named after the Greek astronomer and mathematician Ptolemy. The four points can be ordered in any of three distinct ways (counting reversals as not distinct) to form three different quadrilaterals, for each of which the sum of the products of opposite sides is at least as large as the product of the diagonals. Thus the three product terms in the inequality can be additively permuted to put any one of them on the right side of the inequality, so the three products of opposite sides or of diagonals of any one of the quadrilaterals must obey the triangle inequality. As a special case, Ptolemy's theorem states that the inequality becomes an equality when the four points lie in cyclic order on a circle.The other case of equality occurs when the four points are collinear in order. The inequality does not generalize from Euclidean spaces to arbitrary metric spaces. The spaces where it remains valid are called the Ptolemaic spaces; they include the inner product spaces, Hadamard spaces, and shortest path distances on Ptolemaic graphs. (Wikipedia).