
What is a line segment and ray
👉 Learn essential definitions of points, lines, and planes. A point defines a position in space. A line is a set of points. A line can be created by a minimum of two points. A plane is a flat surface made up of at least three points. A plane contains infinite number of lines. A ray is a li
From playlist Points Lines and Planes

👉 Learn essential definitions of points, lines, and planes. A point defines a position in space. A line is a set of points. A line can be created by a minimum of two points. A plane is a flat surface made up of at least three points. A plane contains infinite number of lines. A ray is a li
From playlist Points Lines and Planes

👉 Learn essential definitions of points, lines, and planes. A point defines a position in space. A line is a set of points. A line can be created by a minimum of two points. A plane is a flat surface made up of at least three points. A plane contains infinite number of lines. A ray is a li
From playlist Points Lines and Planes

👉 Learn essential definitions of points, lines, and planes. A point defines a position in space. A line is a set of points. A line can be created by a minimum of two points. A plane is a flat surface made up of at least three points. A plane contains infinite number of lines. A ray is a li
From playlist Points Lines and Planes

👉 Learn essential definitions of points, lines, and planes. A point defines a position in space. A line is a set of points. A line can be created by a minimum of two points. A plane is a flat surface made up of at least three points. A plane contains infinite number of lines. A ray is a li
From playlist Points Lines and Planes

What is a point a line and a plane
👉 Learn essential definitions of points, lines, and planes. A point defines a position in space. A line is a set of points. A line can be created by a minimum of two points. A plane is a flat surface made up of at least three points. A plane contains infinite number of lines. A ray is a li
From playlist Points Lines and Planes

👉 Learn essential definitions of points, lines, and planes. A point defines a position in space. A line is a set of points. A line can be created by a minimum of two points. A plane is a flat surface made up of at least three points. A plane contains infinite number of lines. A ray is a li
From playlist Points Lines and Planes

👉 Learn essential definitions of points, lines, and planes. A point defines a position in space. A line is a set of points. A line can be created by a minimum of two points. A plane is a flat surface made up of at least three points. A plane contains infinite number of lines. A ray is a li
From playlist Points Lines and Planes

How to determine the distance from a point to a line. The ideas involve projection of vectors. Free ebook https://bookboon.com/en/introduction-to-vectors-ebook (updated link) Test your understanding via a short quiz http://goo.gl/forms/wHGVJKuSvu
From playlist Introduction to Vectors
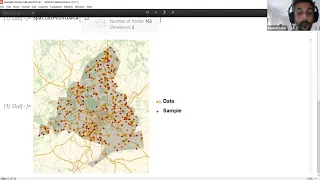
Spatial point data, also known as spatial point patterns, refers to collections of points (or events) in space. Examples include trees in a forest, gold deposits, positions of stars, earthquakes, crime locations, animal sightings, etc. The aim of spatial point data modeling is to capture t
From playlist Wolfram Technology Conference 2020

Spatial Events: Spatial Statistics
Spatial point patterns are collections of randomly positioned events in space. Examples include trees in a forest, positions of stars, earthquakes, crime locations, animal sightings, etc. Spatial point data analysis, as a statistical exploration of point patterns, aims to answer questions
From playlist Wolfram Technology Conference 2021

Limit Theorems for Spatial Interacting Models by Yogeshwaran D
PROGRAM: TOPICS IN HIGH DIMENSIONAL PROBABILITY ORGANIZERS: Anirban Basak (ICTS-TIFR, India) and Riddhipratim Basu (ICTS-TIFR, India) DATE & TIME: 02 January 2023 to 13 January 2023 VENUE: Ramanujan Lecture Hall This program will focus on several interconnected themes in modern probab
From playlist TOPICS IN HIGH DIMENSIONAL PROBABILITY

Adrian Baddeley: The Poisson-saddlepoint approximation
Gibbs spatial point processes are important models in theoretical physics and in spatial statistics. After a brief survey of Gibbs point processes, we will present a method for approximating their most important characteristic, the intensity of the process. The method has some affinity wit
From playlist Probability and Statistics

Branching Random Walk and Regular variation by Rajat Subhra Hazra
Large deviation theory in statistical physics: Recent advances and future challenges DATE: 14 August 2017 to 13 October 2017 VENUE: Madhava Lecture Hall, ICTS, Bengaluru Large deviation theory made its way into statistical physics as a mathematical framework for studying equilibrium syst
From playlist Large deviation theory in statistical physics: Recent advances and future challenges

Spatial Point Data and Processes
To learn more about Wolfram Technology Conference, please visit: https://www.wolfram.com/events/technology-conference/ Speaker: Gosia Konwerska & Eduardo Serna Wolfram developers and colleagues discussed the latest in innovative technologies for cloud computing, interactive deployment, m
From playlist Wolfram Technology Conference 2018
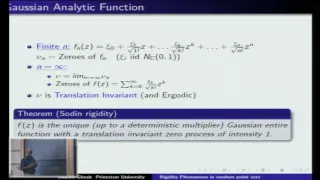
Rigidity phenomena in random point sets and applications - Subhroshekhar Ghosh
Subhroshekhar Ghosh Princeton University December 11, 2013 In several naturally occurring (infinite) point processes, we show that the number (and other statistical properties) of the points inside a finite domain are determined, almost surely, by the point configuration outside the domain
From playlist Mathematics

Anne Marie Svane (12/14/2022): Analyzing point processes using topological data analysis
Abstract: Topological data analysis has become a popular tool in spatial statistics for analyzing point processes. This talk will introduce some of the standard models for point processes and indicate how topological data analysis can be used to distinguish between different types of model
From playlist AATRN 2022

Omer Angel (UBC) -- A tale of two balloons
We study the following process, motivated by coalescing random walks: From each point of a Poisson point process start growing a balloon at rate 1. When two balloons touch, they pop and disappear. We study this on various spaces and various starting states. En route we find a new(ish) 0-1
From playlist Columbia Probability Seminar

Mylène Maïda: A statistical physics approach to the sine beta process
The universality properties of the Sine process (corresponding to inverse temperature beta equal to 2) are now well known. More generally, a family of point processes have been introduced by Valko and Virag and shown to be the bulk limit of Gaussian beta ensembles, for any positive beta. T
From playlist Probability and Statistics

What is a point line and plane
👉 Learn essential definitions of points, lines, and planes. A point defines a position in space. A line is a set of points. A line can be created by a minimum of two points. A plane is a flat surface made up of at least three points. A plane contains infinite number of lines. A ray is a li
From playlist Points Lines and Planes