Rotational symmetry | Tensors | Angle
Angular velocity
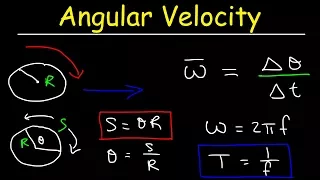
In physics, angular velocity or rotational velocity (ω or Ω), also known as angular frequency vector, is a pseudovector representation of how fast the angular position or orientation of an object changes with time (i.e. how quickly an object rotates or revolves relative to a point or axis). The magnitude of the pseudovector represents the angular speed, the rate at which the object rotates or revolves, and its direction is normal to the instantaneous plane of rotation or angular displacement. The orientation of angular velocity is conventionally specified by the right-hand rule. There are two types of angular velocity. * Orbital angular velocity refers to how fast a point object revolves about a fixed origin, i.e. the time rate of change of its angular position relative to the origin. * Spin angular velocity refers to how fast a rigid body rotates with respect to its center of rotation and is independent of the choice of origin, in contrast to orbital angular velocity. In general, angular velocity has dimension of angle per unit time (angle replacing distance from linear velocity with time in common). The SI unit of angular velocity is radians per second, with the radian being a dimensionless quantity, thus the SI units of angular velocity may be listed as s−1. Angular velocity is usually represented by the symbol omega (ω, sometimes Ω). By convention, positive angular velocity indicates counter-clockwise rotation, while negative is clockwise. For example, a geostationary satellite completes one orbit per day above the equator, or 360 degrees per 24 hours, and has angular velocity ω = (360°)/(24 h) = 15°/h, or (2π rad)/(24 h) ≈ 0.26 rad/h. If angle is measured in radians, the linear velocity is the radius times the angular velocity, . With orbital radius 42,000 km from the earth's center, the satellite's speed through space is thus v = 42,000 km × 0.26/h ≈ 11,000 km/h. The angular velocity is positive since the satellite travels eastward with the Earth's rotation (counter-clockwise from above the north pole.) (Wikipedia).