
Mark Sapir - The Tarski numbers of groups.
Mark Sapir (Vanderbilt University, USA) The Tarski number of a non-amenable group is the minimal number of pieces in a paradoxical decomposition of the group. It is known that a group has Tarski number 4 if and only if it contains a free non-cyclic subgroup, and the Tarski numbers of tors
From playlist T1-2014 : Random walks and asymptopic geometry of groups.

Unpredictability, Undecidability, and Uncomputability
Quite a number of mathematical theorems prove that the power of mathematics has its limits. But how relevant are these theorems for science? In this video I want to briefly summarize an essay that I just submitted to the essay contest of the Foundational Questions Institute. This year the
From playlist Philosophy of Science

Silvia Steila: An overview over least fixed points in weak set theories
Given a monotone function on a complete lattice the least fixed point is defined as the minimum among the fixed points. Tarski Knaster Theorem states that every monotone function on a complete lattice has a least fixed point. There are two standard proofs of Tarski Knaster Theorem. The f
From playlist Workshop: "Proofs and Computation"

This Math Theorem Proves that 1=1+1 | The Banach-Tarskis Paradox
Mathematicians are in nearly universal agreement that the strangest paradox in math is the Banach-Tarski paradox, in which you can split one ball into a finite number of pieces, then rearrange the pieces to get two balls of the same size. Interestingly, only a minority of mathematicians ha
From playlist Math and Statistics
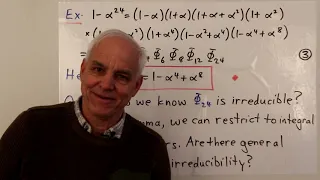
Irreducibility and the Schoenemann-Eisenstein criterion | Famous Math Probs 20b | N J Wildberger
In the context of defining and computing the cyclotomic polynumbers (or polynomials), we consider irreducibility. Gauss's lemma connects irreducibility over the integers to irreducibility over the rational numbers. Then we describe T. Schoenemann's irreducibility criterion, which uses some
From playlist Famous Math Problems

Video3-4: Existence and Uniqueness Them; Definition of Wronskian. Elementary Differential Equations
Elementary Differential Equations Video3-4: Existence and Uniqueness Theorem; the Definition and applications of Wronskian on linear dependence Course playlist: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLbxFfU5GKZz0GbSSFMjZQyZtCq-0ol_jD
From playlist Elementary Differential Equations

Differential Equations | Undetermined Coefficients for a System of DEs
We use the method of undetermined coefficients to solve a nonhomogeneous system of first order linear differential equations. http://www.michael-penn.net http://www.randolphcollege.edu/mathematics/
From playlist Systems of Differential Equations

Alina Ostafe: Dynamical irreducibility of polynomials modulo primes
Abstract: In this talk we look at polynomials having the property that all compositional iterates are irreducible, which we call dynamical irreducible. After surveying some previous results (mostly over finite fields), we will concentrate on the question of the dynamical irreducibility of
From playlist Number Theory Down Under 9
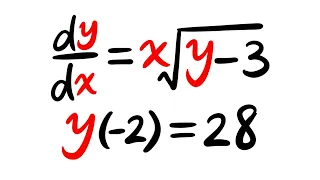
Existence & Uniqueness Theorem, Ex1.5
Existence & Uniqueness Theorem for differential equations. Subscribe for more math for fun videos 👉 https://bit.ly/3o2fMNo For more calculus & differential equation tutorials, check out @justcalculus 👉 https://www.youtube.com/justcalculus To learn how to solve different types of d
From playlist Differential Equations: Existence & Uniqueness Theorem (Nagle Sect1.2)

Measurable equidecompositions – András Máthé – ICM2018
Analysis and Operator Algebras Invited Lecture 8.8 Measurable equidecompositions András Máthé Abstract: The famous Banach–Tarski paradox and Hilbert’s third problem are part of story of paradoxical equidecompositions and invariant finitely additive measures. We review some of the classic
From playlist Analysis & Operator Algebras

Kurt Gödel Centenary - Part III
John W. Dawson, Jr. Pennsylvania State University November 17, 2006 More videos on http://video.ias.edu
From playlist Kurt Gödel Centenary
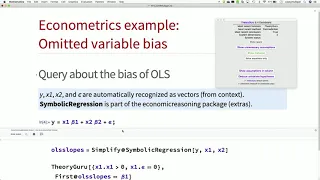
Automated Economic Reasoning with Mathematica
Casey Mulligan
From playlist Wolfram Technology Conference 2019

Joel David Hamkins : The hierarchy of second-order set theories between GBC and KM and beyond
Abstract: Recent work has clarified how various natural second-order set-theoretic principles, such as those concerned with class forcing or with proper class games, fit into a new robust hierarchy of second-order set theories between Gödel-Bernays GBC set theory and Kelley-Morse KM set th
From playlist Logic and Foundations

Robert Ghrist (8/29/21): Laplacians and Network Sheaves
This talk will begin with a simple introduction to cellular sheaves as a generalized notion of a network of algebraic objects. With a little bit of geometry, one can often define a Laplacian for such sheaves. The resulting Hodge theory relates the geometry of the Laplacian to the algebraic
From playlist Beyond TDA - Persistent functions and its applications in data sciences, 2021

Support Vsauce, your brain, Alzheimer's research, and other YouTube educators by joining THE CURIOSITY BOX: a seasonal delivery of viral science toys made by Vsauce! A portion of all proceeds goes to Alzheimer's research and our Inquisitive Fellowship, a program that gives money and resour
From playlist Science

Matthew Foreman: Welch games to Laver ideals
Recorded during the meeting "XVI International Luminy Workshop in Set Theory" the September 16, 2021 by the Centre International de Rencontres Mathématiques (Marseille, France) Filmmaker: Guillaume Hennenfent Find this video and other talks given by worldwide mathematicians on CIRM's Au
From playlist Logic and Foundations

Death by infinity puzzles and the Axiom of Choice
In this video the Mathologer sets out to commit the perfect murder using infinitely many assassins and, subsequently, to get them off the hook in court. The story is broken up into three very tricky puzzles. Challenge yourself to figure them out before the Mathologer reveals his own soluti
From playlist Recent videos

How to Determine if Functions are Linearly Independent or Dependent using the Definition
How to Determine if Functions are Linearly Independent or Dependent using the Definition If you enjoyed this video please consider liking, sharing, and subscribing. You can also help support my channel by becoming a member https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCr7lmzIk63PZnBw3bezl-Mg/join Th
From playlist Zill DE 4.1 Preliminary Theory - Linear Equations