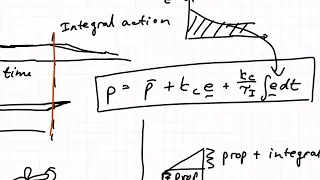
Proportional control
Proportional control, in engineering and process control, is a type of linear feedback control system in which a correction is applied to the controlled variable, and the size of the correction is proportional to the difference between the desired value (setpoint, SP) and the measured value (process variable, PV). Two classic mechanical examples are the toilet bowl float proportioning valve and the fly-ball governor. The proportional control concept is more complex than an on–off control system such as a bi-metallic domestic thermostat, but simpler than a proportional–integral–derivative (PID) control system used in something like an automobile cruise control. On–off control will work where the overall system has a relatively long response time, but can result in instability if the system being controlled has a rapid response time. Proportional control overcomes this by modulating the output to the controlling device, such as a control valve at a level which avoids instability, but applies correction as fast as practicable by applying the optimum quantity of proportional gain. A drawback of proportional control is that it cannot eliminate the residual SP − PV error in processes with compensation e.g. temperature control, as it requires an error to generate a proportional output. To overcome this the PI controller was devised, which uses a proportional term (P) to remove the gross error, and an integral term (I) to eliminate the residual offset error by integrating the error over time to produce an "I" component for the controller output. (Wikipedia).