
Proof: What is it, and how does it work?
From playlist The Nature of Proof

Introduction to the Nature of Proof (3 of 3: Liars & truth-tellers)
More resources available at www.misterwootube.com
From playlist The Nature of Proof

How to determine the truth table from a statement and determine its validity
👉 Learn how to determine the truth or false of a conditional statement. A conditional statement is an if-then statement connecting a hypothesis (p) and the conclusion (q). If the hypothesis of a statement is represented by p and the conclusion is represented by q, then the conditional stat
From playlist Conditional Statements

A Brief Introduction to Proofs
This video serves as an introduction to proofs.
From playlist Summer of Math Exposition Youtube Videos

How many subsets in a set? (1 of 2: Induction proof)
More resources available at www.misterwootube.com
From playlist The Nature of Proof

Lec 1 | MIT 6.042J Mathematics for Computer Science, Fall 2010
Lecture 1: Introduction and Proofs Instructor: Tom Leighton View the complete course: http://ocw.mit.edu/6-042JF10 License: Creative Commons BY-NC-SA More information at http://ocw.mit.edu/terms More courses at http://ocw.mit.edu
From playlist MIT 6.042J Mathematics for Computer Science, Fall 2010

7. Ch. 3, Sections 3.1 & 3.2. Introduction to Logic, Philosophy 10, UC San Diego - BSLIF
Video lecture corresponding to _Basic Sentential Logic and Informal Fallacies_, Chapter 3, Sections 3.1 & 3.2. This is for the class Introduction to Logic, Philosophy 10, UC San Diego.
From playlist UC San Diego: PHIL 10 - Introduction to Logic | CosmoLearning.org Philosophy

What are the basics of mathematical logic? | Intro to Math Structures VS1.1
So you want to prove things? Where do you start if you haven't ever written a proof before? In most cases, a course on discrete mathematics or mathematical structures is where someone writes their first proof and that starts with propositional calculus. In this video section, we go through
From playlist The CHALKboard 2022

Defining and comprehending "implication" in Mathematics
I'm not a native English speaker, sorry about my pronunciation and fluency in English. If there is any kind of mistake in the video, please inform me in the comments section.
From playlist Summer of Math Exposition Youtube Videos

Proof-of-Work — Waste of energy or useful?
Bitcoin mining uses proof of work to determine its supply issuance. Many people believe proof of work should be replaced by proof of stake due to its energy usage. But is that really the case? There is a whole other side that believes proof of work is useful. Who is right? ₿ Donate using
From playlist Summer of Math Exposition Youtube Videos

Billy Price and Will Troiani present a series of seminars on foundations of mathematics. In this seminar Billy introduces natural deduction as a proof system. You can join this seminar from anywhere, on any device, at https://www.metauni.org. This video was filmed in Deprecation (https:/
From playlist Foundations seminar

The Mathematical Truth | Enrico Bombieri
Enrico Bombieri, Professor Emeritus, School of Mathematics, Institute for Advanced Study http://www.ias.edu/people/faculty-and-emeriti/bombieri October 29, 2010 In this lecture, Professor Enrico Bombieri attempts to give an idea of the numerous different notions of truth in mathematics.
From playlist Mathematics

Inference: A Logical-Philosophical Perspective - Moderated Conversation w/ A.C. Paseau and Gila Sher
Inference: A Logical-Philosophical Perspective. Moderated Conversation with Gila Sher, Department of Philosophy, University of California, San Diego on the talk by Alexander Paseau, Faculty of Philosophy, University of Oxford. The Franke Program in Science and the Humanities Understandi
From playlist Franke Program in Science and the Humanities
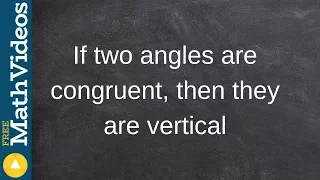
How to determine the truth of a statement using a truth table
👉 Learn how to determine the truth or false of a conditional statement. A conditional statement is an if-then statement connecting a hypothesis (p) and the conclusion (q). If the hypothesis of a statement is represented by p and the conclusion is represented by q, then the conditional stat
From playlist Conditional Statements

How to determine the truth of a statement using a truth table
👉 Learn how to determine the truth or false of a conditional statement. A conditional statement is an if-then statement connecting a hypothesis (p) and the conclusion (q). If the hypothesis of a statement is represented by p and the conclusion is represented by q, then the conditional stat
From playlist Conditional Statements

Undertale Propositional Logic (#SoME2)
I'm sorry I had to do it because of the memes. Crash course educational look of propositional logic with the motivation to show how to prove things through proof by contradiction and proof by contraposition. Honorable shoutouts to @blackpenredpen and @drpeyam. God bless Toby Fox! Timel
From playlist Summer of Math Exposition 2 videos



