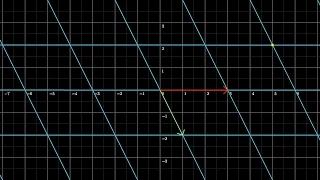
👉 Learn about graphing linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. i.e. linear equations has no exponents on their variables. The graph of a linear equation is a straight line. To graph a linear equation, we identify two values (x-valu
From playlist ⚡️Graph Linear Equations | Learn About

Summary for graph an equation in Standard form
👉 Learn about graphing linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. i.e. linear equations has no exponents on their variables. The graph of a linear equation is a straight line. To graph a linear equation, we identify two values (x-valu
From playlist ⚡️Graph Linear Equations | Learn About

How to graph a linear equation in Standard form
👉 Learn about graphing linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. i.e. linear equations has no exponents on their variables. The graph of a linear equation is a straight line. To graph a linear equation, we identify two values (x-valu
From playlist ⚡️Graph Linear Equations | Learn About

What is the parent function of a linear graph
👉 Learn about graphing linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. i.e. linear equations has no exponents on their variables. The graph of a linear equation is a straight line. To graph a linear equation, we identify two values (x-valu
From playlist ⚡️Graph Linear Equations | Learn About

👉 Learn about graphing linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. i.e. linear equations has no exponents on their variables. The graph of a linear equation is a straight line. To graph a linear equation, we identify two values (x-valu
From playlist ⚡️Graph Linear Equations | Learn About

What is the slope of a linear equation
👉 Learn about graphing linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. i.e. linear equations has no exponents on their variables. The graph of a linear equation is a straight line. To graph a linear equation, we identify two values (x-valu
From playlist ⚡️Graph Linear Equations | Learn About

👉 Learn about graphing linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. i.e. linear equations has no exponents on their variables. The graph of a linear equation is a straight line. To graph a linear equation, we identify two values (x-valu
From playlist ⚡️Graph Linear Equations | Learn About

What are the x and y intercepts of a linear equation
👉 Learn about graphing linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. i.e. linear equations has no exponents on their variables. The graph of a linear equation is a straight line. To graph a linear equation, we identify two values (x-valu
From playlist ⚡️Graph Linear Equations | Learn About

Machine Learning Algorithms In-Depth Guide For 2022 | ML Algorithms Explained | Simplilearn
This video on Machine Learning Algorithm will take you through a detailed concept of machine learning algorithm. This video will help you to understand What is an Algorithm, What is Machine Learning, Types of Machine Learning, How Algorithms works in Machine Learning/Programing, Some popul

Conditional Average Treatment Effects: Forests
Professor Susan Athey discusses causal forests in conditional average treatment effects.
From playlist Machine Learning & Causal Inference: A Short Course
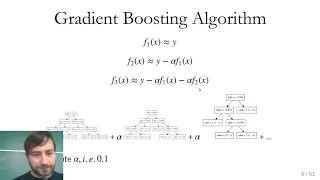
Applied Machine Learning 2019 - Lecture 09 - Gradient boosting; Calibration
Gradient boosting and "extreme" gradient boosting Calibration curves and calibrating classifiers with CalibratedClassifierCV. Class website with slides and more materials: https://www.cs.columbia.edu/~amueller/comsw4995s19/schedule/
From playlist Applied Machine Learning - Spring 2019

The Best Way to Predict NBA Minutes Played
Hey All! I use a systematic approach to find best predictor of NBA Minutes Played. I have recently gotten into daily fantasy basketball. Many experts suggest that minutes played is highly correlated with daily fantasy points. The basic equation is Projected Minutes Played * Avg FTPS per
From playlist Data Science Projects

Today we start the second half of the course - we're moving from decision tree based approaches like random forests, to gradient descent based approaches like deep learning. Our first step in this journey will be to use Pytorch to help us implement logistic regression from scratch. We'll
From playlist Introduction to Machine Learning for Coders

Fake Job Listing Detection Tutorial | Python Projects | Data Science Training | Edureka
🔥Machine Learning Engineer Masters Program: https://www.edureka.co/masters-program/machine-learning-engineer-training This Edureka video on "Fake Job Listing Detection” will provide you with comprehensive and detailed knowledge of Machine Learning concepts with a hands-on project where you
From playlist Machine Learning Algorithms in Python (With Demo) | Edureka

Giles Hooker - Ensembles of Trees and CLT's: Inference and Machine Learning
Professor Giles Hooker (Australian National University) presents "Ensembles of Trees and CLT's: Inference and Machine Learning", 14 May 2020. This seminar was organised by the Australian National University.
From playlist Statistics Across Campuses

Large scale non-linear learning on a single CPU
Andreas Mueller http://www.pyvideo.org/video/3809/large-scale-non-linear-learning-on-a-single-cpu https://pygotham.org/2015/talks/146/large-scale-non-linear-learning-on-a-single-cpu This talk presents several methods for learning non-linear models on a single machine, where the dataset doe
From playlist talks

What do I need to know to graph an equation in standard form
👉 Learn about graphing linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. i.e. linear equations has no exponents on their variables. The graph of a linear equation is a straight line. To graph a linear equation, we identify two values (x-valu
From playlist ⚡️Graph Linear Equations | Learn About

Average Treatment Effects: Confounding
Professor Stefan Wager on confounding and regression adjustments. Comparison of regression adjustments done via OLS versus generic machine learning.
From playlist Machine Learning & Causal Inference: A Short Course