Measure theory | Statistical distance | Theory of probability distributions | Metric geometry
Wasserstein metric
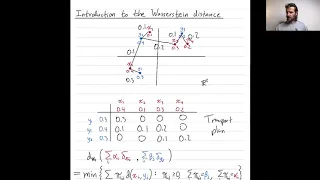
In mathematics, the Wasserstein distance or Kantorovich–Rubinstein metric is a distance function defined between probability distributions on a given metric space . It is named after Leonid Vaseršteĭn. Intuitively, if each distribution is viewed as a unit amount of earth (soil) piled on , the metric is the minimum "cost" of turning one pile into the other, which is assumed to be the amount of earth that needs to be moved times the mean distance it has to be moved. This problem was first formalised by Gaspard Monge in 1781. Because of this analogy, the metric is known in computer science as the earth mover's distance. The name "Wasserstein distance" was coined by R. L. Dobrushin in 1970, after learning of it in the work of Leonid Vaseršteĭn on Markov processes describing large systems of automata (Russian, 1969). However the metric was first defined by Leonid Kantorovich in The Mathematical Method of Production Planning and Organization (Russian original 1939) in the context of optimal transport planning of goods and materials. Some scholars thus encourage use of the terms "Kantorovich metric" and "Kantorovich distance". Most English-language publications use the German spelling "Wasserstein" (attributed to the name "Vaseršteĭn" being of German origin). (Wikipedia).