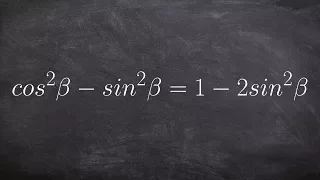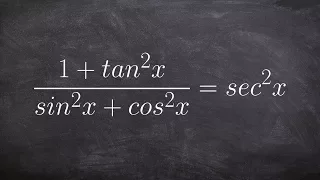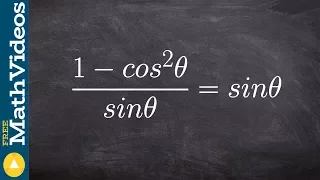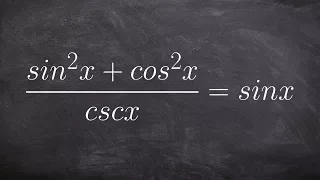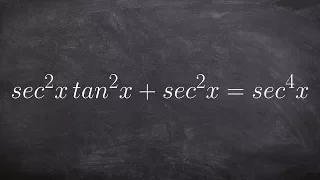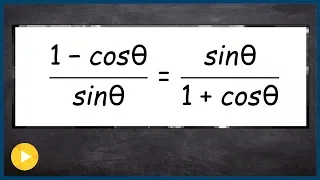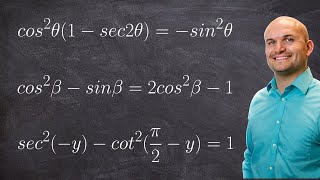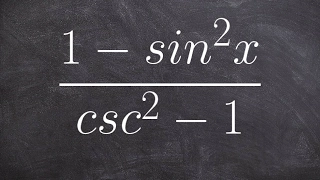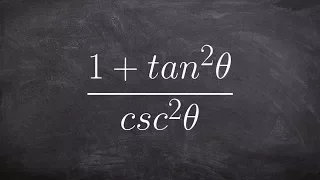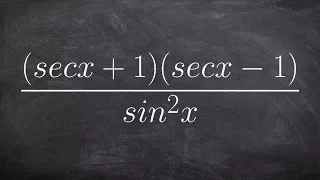Pythagorean theorem | Articles containing proofs | Mathematical identities | Trigonometry
Pythagorean trigonometric identity
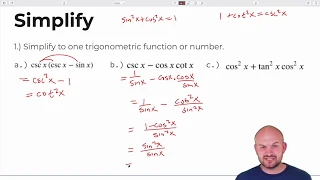
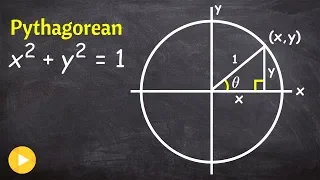
The Pythagorean trigonometric identity, also called simply the Pythagorean identity, is an identity expressing the Pythagorean theorem in terms of trigonometric functions. Along with the sum-of-angles formulae, it is one of the basic relations between the sine and cosine functions. The identity is As usual, sin2 θ means . (Wikipedia).