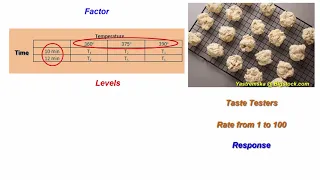
Overview of Experimental Design
From playlist Unit 4: Sampling and Experimental Design

Percentiles, Deciles, Quartiles
Understanding percentiles, quartiles, and deciles through definitions and examples
From playlist Unit 1: Descriptive Statistics
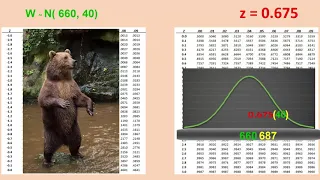
Determining values of a variable at a particular percentile in a normal distribution
From playlist Unit 2: Normal Distributions

More Standard Deviation and Variance
Further explanations and examples of standard deviation and variance
From playlist Unit 1: Descriptive Statistics
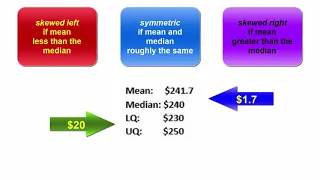
Mean v Median and the implications
Differences between the mean and median suggest the presence of outliers and/or the possible shape of a distribution
From playlist Unit 1: Descriptive Statistics

Operating system for beginners || Operating system basics
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common services for computer programs. Time-sharing #operating_systems schedule tasks for efficient use of the system and may also include accounting software for cost allocation o
From playlist Operating System

FROGS Find Rapidly OTU with Galaxy Solution, 20160628
Galaxy Community Conference 2016, Indiana University - Bloomington | https://gcc2016.iu.edu/ https://gcc16.sched.com/event/3708f8eb14531cffedf3c29aed075a43# Authors: Frederic ESCUDIE, INRA Toulouse Lucas AUER, INRA Toulouse Maria BERNARD, INRA Jouy-en-Josas Laurent CAUQUIL, INRA Toulouse
From playlist 2016 Galaxy User Community Conference (GCC16)

David Koslicki: "The CAMI Project: Assessment of computational techniques in metagenomics"
Computational Genomics Summer Institute 2017 Tutorial: "The CAMI Project: Assessment of computational techniques in metagenomics" David Koslicki, Oregon State University Institute for Pure and Applied Mathematics, UCLA July 12, 2017 For more information: http://computationalgenomics.bio
From playlist Computational Genomics Summer Institute 2017

Moodle - Add an Assignment activity
From playlist Training - Moodle
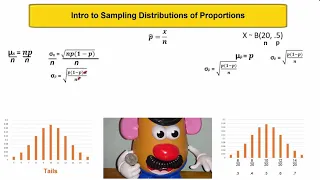
An overview and introduction to understanding sampling distributions of proportions [sample proportions] and how to calculate them
From playlist Unit 7 Probability C: Sampling Distributions & Simulation
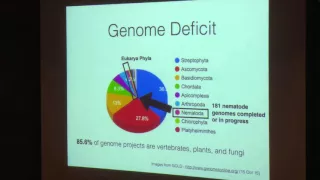
Evolution, Biogeography and "Systems Ecology" in Microbial Eukaryote Taxa - H. Bik - 1/14/16
Bioinformatics Research Symposium Beckman Institute Auditorium Thursday, January 14, 2016
From playlist Bioinformatics Research Symposium

Elizabeth Ramirez - Graph Database Patterns in Python - PyCon 2015
"Speaker: Elizabeth Ramirez Creating and using models from a graph database can be quite different to the ones used for row/column/document-oriented databases, in the sense that the same query patterns could differ significantly in structure and performance. This session will present how
From playlist Software Development Lectures

Live CEOing Ep 681: Language Design in Wolfram Language [Ontologies]
In this episode of Live CEOing, Stephen Wolfram discusses upcoming improvements and features to the Wolfram Language. If you'd like to contribute to the discussion in future episodes, you can participate through this YouTube channel or through the official Twitch channel of Stephen Wolfram
From playlist Behind the Scenes in Real-Life Software Design

Why Hardwoods Are The Softest Woods
Use the promo code "minuteearth" at https://curiositystream.com/minuteearth for 26% off an annual subscription to CuriosityStream, plus access to Nebula! Not all hardwood trees have hard wood and softwoods soft wood, because these terms denote their taxonomic ancestry, not the wood's actu
From playlist Evolution
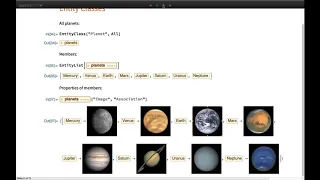
Knowledgebase Query Language and Entities
This webinar features talks that demonstrate how Version 12 of the Wolfram Language extends the capabilities of the entity framework, with a deeper look at food and nutrition data, cultural and historical entities and computable knowledge in biology and medicine. This is the second webinar
From playlist New in Wolfram Language 12 Webinar Series
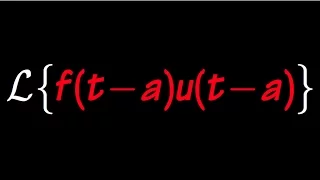
Laplace transform of f(t-a)u(t-a), the shifted unit step function
laplace transform of unit step function, Laplace transform of f(t-a)u(t-a), Laplace transform of the shifted unit step function, Laplace transform of f(t)u(t-a), Translation in t theorem, differential equation and laplace transform, www.blackpenredpen.com
From playlist Unit Step Functions & Translation in t (Nagle Sect7.6)
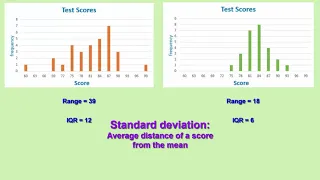
Introduction to standard deviation, IQR [Inter-Quartile Range], and range
From playlist Unit 1: Descriptive Statistics

New Biology Content in the Wolfram Language
Wolfram technology provides access to a diverse range of computable knowledge about biology. In this talk, topics such as taxonomic classifications, dinosaurs and genomics are explored as examples of the breadth of information available in the Wolfram Language. The latest taxonomic data co
From playlist Wolfram Technology Conference 2022