
What is a Four-Vector? Is a Spinor a Four-Vector? | Special Relativity
In special relativity, we are dealing a lot with four-vectors, but what exactly is a four-vector? A four-vector is an object with four entries, which get transformed and changed in a very special way after we change our frame of reference. More precisely, a four-vector transforms like a (1
From playlist Special Relativity, General Relativity

For more information about Professor Shankar's book based on the lectures from this course, Fundamentals of Physics: Mechanics, Relativity, and Thermodynamics, visit http://bit.ly/1jFIqNu. Fundamentals of Physics (PHYS 200) The discussion of four-vector in relativity continues but this t
From playlist Fundamentals of Physics with Ramamurti Shankar
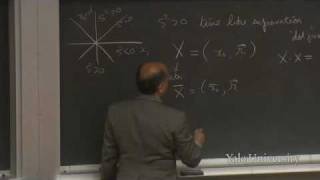
14. Introduction to the Four-Vector
For more information about Professor Shankar's book based on the lectures from this course, Fundamentals of Physics: Mechanics, Relativity, and Thermodynamics, visit http://bit.ly/1jFIqNu. Fundamentals of Physics (PHYS 200) The four-vector is introduced that unifies space-time coordinate
From playlist Fundamentals of Physics with Ramamurti Shankar

What is the 4th Dimension REALLY? - 4D Golf Devlog #2
A more practical explanation for those interested in exploring 4D spaces. For those not already familiar with basic 4D concepts, here's some videos I can recommend: "Visualizing 4D Geometry" https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4URVJ3D8e8k "The things you'll find in higher dimensions" https:/
From playlist 4D Golf

The Definition of a Linear Equation in Two Variables
This video defines a linear equation in to variables and provides examples of the different forms of linear equations. http://mathispower4u.com
From playlist The Coordinate Plane, Plotting Points, and Solutions to Linear Equations in Two Variables

Acceleration in Special Relativity | Four-Acceleration
In this video, we will explain acceleration in special relativity. In classical mechanics, acceleration is defined as the time derivative of the velocity vector. In special relativity, we use a similar equation, but instead of a time derivative, we use a derivative with respect to the pr
From playlist Special Relativity, General Relativity

Can You Solve This THREE Dimensional Physics Problem?!?? #Physics #Mechanics #Engineering #3D #NicholasGKK #Shorts
From playlist General Mechanics

System of Equations with Three Equations and Three Variables
Please Subscribe here, thank you!!! https://goo.gl/JQ8Nys System of Equations with Three Equations and Three Variables
From playlist Systems of Equations

Drawing the 4th, 5th, 6th, and 7th dimension
How to draw 4, 5, 6, and 7 dimensional objects.
From playlist Physics

AP Physics 1 review of 1D motion
In this video David rapidly explains all the concepts in 1D motion and also quickly solves a sample problem for each concept. Click on and keep an eye on the side scroll to go to the topic you want and to see how far along you've made it in the review video. Here's a link to download the
From playlist Review for AP Physics 1 exam | AP Physics 1 | Khan Academy

Lecture 6 | Quantum Entanglements, Part 3 (Stanford)
Lecture 6 of Leonard Susskind's course concentrating on Quantum Entanglements (Part 3, Spring 2007). Recorded May 14, 2007 at Stanford University. This Stanford Continuing Studies course is the third of a three-quarter sequence of classes exploring the "quantum entanglements" in modern
From playlist Lecture Collection | Quantum Entanglements: Part 3 (Spring 2007)

Calculus AB Homework 5.5: Particle Motion Practice
Download Packet: https://goo.gl/Cjrhyr ================================= AP Calculus AB / IB Math SL Unit 5: Existence Theorems and Particle Motion Lesson 5: Particle Motion Practice =================================
From playlist AP Calculus AB

Jet Aircraft Propulsion by Prof. Bhaskar Roy and Prof. A. M. Pradeep, Department of Aerospace Engineering, IIT Bombay. For more details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.iitm.ac.in
From playlist IIT Bombay: Aerospace - Jet Aircraft Propulsion (CosmoLearning Aerospace Engineering)

Average velocity for constant acceleration | One-dimensional motion | Physics | Khan Academy
Calculating average velocity when acceleration is constant. Created by Sal Khan. Watch the next lesson: https://www.khanacademy.org/science/physics/one-dimensional-motion/kinematic-formulas/v/acceleration-of-aircraft-carrier-takeoff?utm_source=YT&utm_medium=Desc&utm_campaign=physics Miss
From playlist One-dimensional motion | AP Physics 1 | Khan Academy

JEE Main Physics E & M #26 Moving Charges in a Magnetic Field
Visit http://ilectureonline.com for more math and science lectures! To donate: http://www.ilectureonline.com/donate https://www.patreon.com/user?u=3236071 A proton, a deuteron and an alpha-particle are moving with the same momentum in a uniform magnetic field. The ratio of magnetic force
From playlist JEE (MAIN) PHYSICS E&M ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM

Given the 2nd Derivative of a Vector Function, Find the Components of r'(t) and r(t)
This video explains how to find the components of a vector function and the components of the derivative of a vector function given the components of the 2nd derivative. http://mathispower4u.com
From playlist Vector Valued Functions

Calculus AB Homework 1.1 Rates of Change
Download Packet: https://goo.gl/WYGSii ================================= AP Calculus AB / IB Math SL Unit 1: Limits and Continuity Lesson 1: Rates of Change =================================
From playlist AP Calculus AB

Lecture 7 | Quantum Entanglements, Part 3 (Stanford)
Lecture 7 of Leonard Susskind's course concentrating on Quantum Entanglements (Part 3, Spring 2007). Recorded May 21, 2007 at Stanford University. This Stanford Continuing Studies course is the third of a three-quarter sequence of classes exploring the "quantum entanglements" in modern
From playlist Lecture Collection | Quantum Entanglements: Part 3 (Spring 2007)

Vector with Magnitude 4 in the Direction of u = (0, 3)
Please Subscribe here, thank you!!! https://goo.gl/JQ8Nys Vector with Magnitude 4 in the Direction of u = (0, 3). We find the vector v with ||v|| = 4 that has the same direction as u = (0, 3).
From playlist Calculus

الميكانيك التقليدي (إم آي تي) 9: مراجعة ما قبل الامتحان الأول
MIT المحاضرة التاسعة من مساق "الميكانيك التقليدي" من جامعة "إم آي تي" للبروفيسور والتر لوين وهي عن: مراجعة ما قبل الامتحان الأول بالإضافة للفيديو هناك ملفات مرفقة على موقعنا الالكتروني https://shamsunalarabia.net/courses/ﺍﻟﻤﻴﻜﺎﻧﻴﻚ-التقليدي/ رابط المساق https://youtu.be/FNooVZcJvG0?list=PL
From playlist 8.01 Arabic Subtitles