Color theory
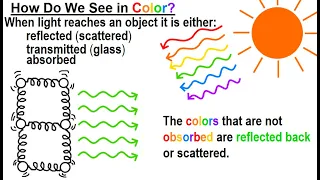
In the visual arts, color theory is the body of practical guidance for color mixing and the visual effects of a specific color combination. Color terminology based on the color wheel and its geometry separates colors into primary color, secondary color, and tertiary color. The understanding of color theory dates to antiquity. Aristotle (d. 322 BCE) and Claudius Ptolemy (d. 168 CE) already discussed which and how colors can be produced by mixing other colors. The influence of light on color was investigated and revealed further by al-Kindi (d. 873) and Ibn al-Haytham (d.1039). Ibn Sina (d. 1037), Nasir al-Din al-Tusi (d. 1274), and Robert Grosseteste (d. 1253) discovered that contrary to the teachings of Aristotle, there are multiple color paths to get from black to white. More modern approaches to color theory principles can be found in the writings of Leone Battista Alberti (c. 1435) and the notebooks of Leonardo da Vinci (c. 1490). A formalization of "color theory" began in the 18th century, initially within a partisan controversy over Isaac Newton's theory of color (Opticks, 1704) and the nature of primary colors. From there it developed as an independent artistic tradition with only superficial reference to colorimetry and vision science. (Wikipedia).