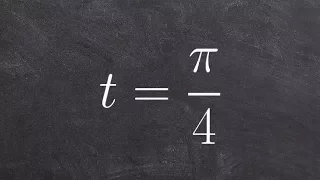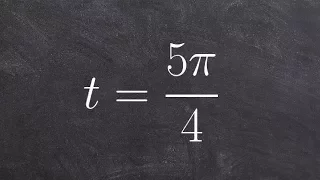Circles of Apollonius
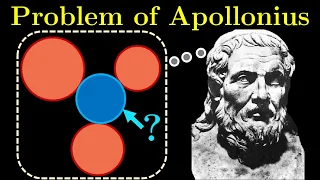
The circles of Apollonius are any of several sets of circles associated with Apollonius of Perga, a renowned Greek geometer. Most of these circles are found in planar Euclidean geometry, but analogs have been defined on other surfaces; for example, counterparts on the surface of a sphere can be defined through stereographic projection. The main uses of this term are fivefold: 1. * Apollonius showed that a circle can be defined as the set of points in a plane that have a specified ratio of distances to two fixed points, known as foci. This Apollonian circle is the basis of the Apollonius pursuit problem. It is a particular case of the first family described in #2. 2. * The Apollonian circles are two families of mutually orthogonal circles. The first family consists of the circles with all possible distance ratios to two fixed foci (the same circles as in #1), whereas the second family consists of all possible circles that pass through both foci. These circles form the basis of bipolar coordinates. 3. * The circles of Apollonius of a triangle are three circles, each of which passes through one vertex of the triangle and maintains a constant ratio of distances to the other two. The isodynamic points and Lemoine line of a triangle can be solved using these circles of Apollonius. 4. * Apollonius' problem is to construct circles that are simultaneously tangent to three specified circles. The solutions to this problem are sometimes called the circles of Apollonius. 5. * The Apollonian gasket—one of the first fractals ever described—is a set of mutually tangent circles, formed by solving Apollonius' problem iteratively. (Wikipedia).