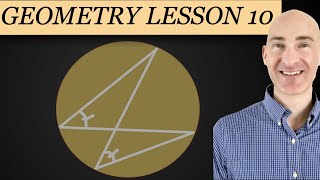
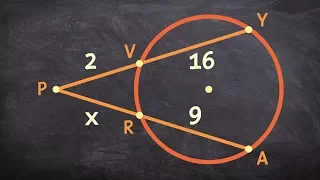Tangent-secant theorem
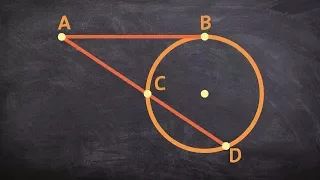
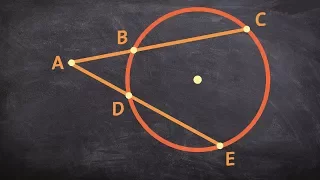
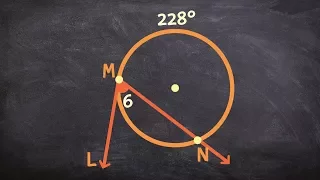
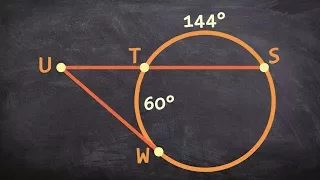
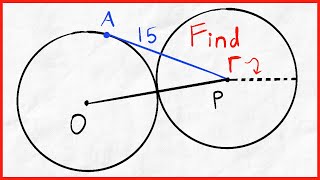
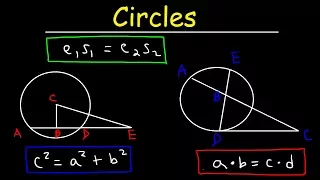
The tangent-secant theorem describes the relation of line segments created by a secant and a tangent line with the associated circle. This result is found as Proposition 36 in Book 3 of Euclid's Elements. Given a secant g intersecting the circle at points G1 and G2 and a tangent t intersecting the circle at point T and given that g and t intersect at point P, the following equation holds: The tangent-secant theorem can be proven using similar triangles (see graphic). Like the intersecting chords theorem and the intersecting secants theorem, the tangent-secant theorem represents one of the three basic cases of a more general theorem about two intersecting lines and a circle, namely, the power of point theorem. (Wikipedia).